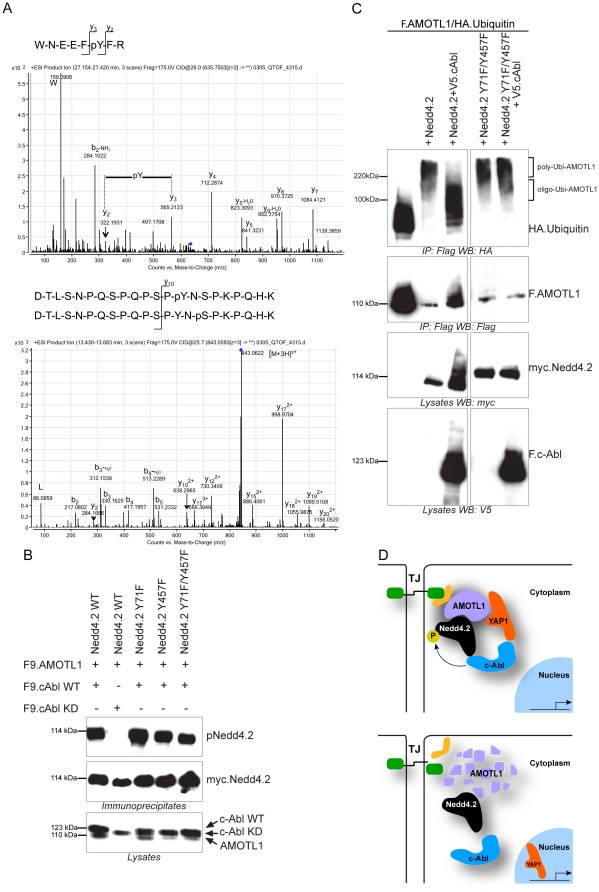
Figure 8. Phosphorylation of Nedd4.2 by c-Abl at tyrosine 71 and 457 inhibits its E3 ligase activity.
A, Myc-Nedd4.2 proteins purified from HEK293T cells, co-expressing either wild type or kinase-dead (KD) c-Abl, were analyzed by nanoLC-MS/MS after in-gel digestion and phosphopeptide enrichment. Two singly Y-phosphorylated peptides (Y71 and Y457) were identified. B, Nedd4.2 proteins with Y71F and Y457F substitutions exhibit moderately reduced levels of c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding myc-tagged wild type (WT) Nedd4.2 or mutants (Y71F, Y457F, or Y71F/Y457F), together with Flag-tagged AMOTL1 and WT or kinase-dead c-Abl, as indicated. Nedd4.2 proteins were precipitated with anti-myc antibodies and blotted with antibodies, as indicated. c-Abl and AMOTL1 were detected in the lysates with anti-Flag antibody. C, c-Abl restricts the ability of Nedd4.2 to extend the poly-ubiquitin chains of AMOTL1. Flag-tagged AMOTL1 (F.AMOTL1) and HA.Ubiquitin were co-expressed with either myc.Nedd4.2 alone, or with myc.Nedd4.2 and V5.cAbl. Ubiquitylated AMOTL1 species, detected by anti-HA antibodies, were shifted from higher molecular weights (poly-Ubi-AMOTL1) above 220 kDa towards lower molecular weight complexes between 100 kDa and 220 kDa (oligo-Ubi-AMOTL1) which are no longer degraded (see text for details). Nedd4.2Y71F/Y457F is resistant to c-Abl phosphorylation. While c-Abl reduced the molecular weight of ubiquitylated AMOTL1 (left panel), there was no detectable change in molecular weight of ubiquitylated AMOTL1 (right panel) when c-Abl was co-expressed with the double tyrosine Nedd4.2 (Nedd4.2 Y71F/Y457F) mutant. D, The dual functions of YAP1. Upper panel: AMOTL1 recruits cytoplasmic YAP1 and c-Abl to tight junctions to curtail the ability of Nedd4.2 to poly-ubiquitylate AMOTL1. Lower panel: In cells primed to undergo proliferation, YAP1 translocates to the nucleus. Now, Nedd4.2 poly-ubiquitylates AMOTL1 and targets it for degradation.