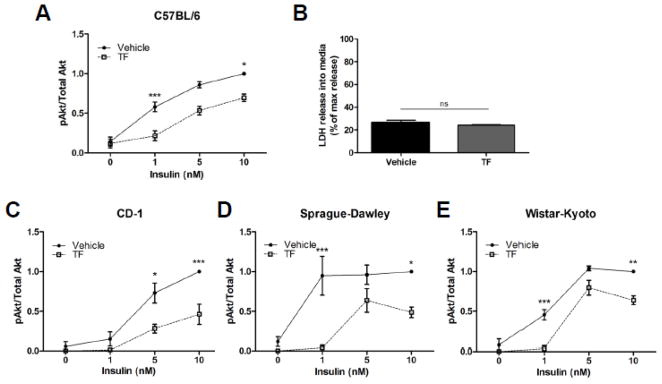
Figure 1.
Effect of TF on insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation in primary rodent adipocytes. Perigonadal depots were sterilely harvested, coarsely minced and incubated with 100 nM TF for 48 h. Cells were then stimulated for 10 min with the indicated concentration of insulin. Lysates were prepared and subjected to anti-phospho-Akt and – total Akt immunoblotting. The phosphorylated-to-total Akt ratio was used to determine insulin action in perigonadal fat pads from male C57BL/6 mice (Panel A; n = 8 except for 5 nM insulin where n = 4), CD-1 mice (Panel C; n = 6 except for 5 nM insulin where n = 4), Sprague-Dawley rats (Panel D; n = 6 except for 5 nM insulin where n = 5), or Wistar-Kyoto rats (Panel E; n = 3). Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. normalized to vehicle-treated adipocytes exposed to 10 nM insulin. Panel B shows LDH release into a media relative to total cellular LDH as a measure of cytotoxicity. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.