Figure 9.
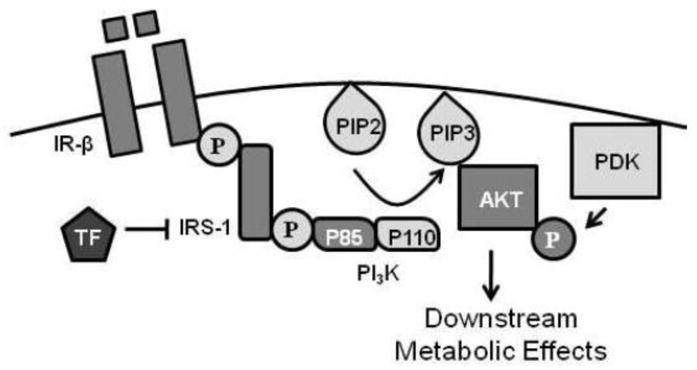
Overview of effects of TF on insulin signal transduction cascade in adipose tissue. Insulin binding to its cell surface receptor (IR) results in auto-transphosphorylation of the two β-subunits and activation of the insulin receptor’s intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity. This leads to tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1, which recruits and activates PI3K through action on the regulatory subunit (p85) leading to the generation of higher ordered lipids (PIP3). Generation of PIP3 recruits Akt to the cell membrane where it is activated by serine/threonine phosphorylation prior to conducting its downstream effects. TF reduces cellular insulin sensitivity by reducing IRS-1 levels, partially through reduction in IRS-1 gene transcription.
