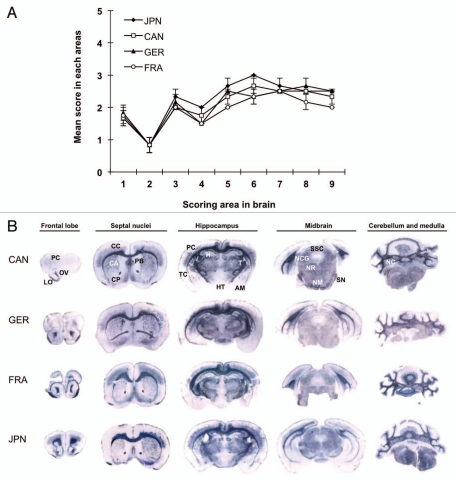
Figure 1.
Neuropathological analysis of L-type BSE isolate-affected TgBoPrP. (A) Lesion profile in the first passage. The vacuolation in the following brain regions was scored on a scale of 0–5 (mean values): 1, dorsal medulla; 2, cerebellar cortex; 3, superior cortex; 4, hypothalamus; 5, thalamus; 6, hippocampus; 7, septal nuclei of the paraterminal body; 8, cerebral cortex at the levels of the hypothalamus and thalamus; and 9, cerebral cortex at the level of the septal nuclei of the paraterminal body. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). ◆, Japanese L-type BSE (JPN); □, Canadian L-type BSE (CAN); ▲, German L-type BSE (GER); ○, French L-type BSE (FRA). (B) The neuroanatomical distribution of PrPSc in the brain of TgBoPrP mice infected with Canadian (CAN), German (GER), French (FRA) and Japanese (JPN) L-type BSE isolate by PET-blot analysis. The PET-blot analysis reveals preferential and intense PrPSc immunolabeling along with periventricular areas, corpus callosum and cerebellar gray matter. Widespread PrPSc immunolabeling is also detected in the thalamic and brainstem nuclei, while PrPSc immunostaining in the cerebral and cerebellar cortices and basal ganglia is less conspicuous. Dewaxed membranes were treated with PK (80 µg/mL), followed by denaturation with 3 M guanidine thiocyanate. The monoclonal antibody (mAb) SAF84 was used. Blots corresponding to the brain areas at the level of frontal lob, septal nuclei, hippocampus, midbrain and medulla and cerebellum. FC, frontal cortex; OV, olfactory ventricle; LO, lateral orbital cortex; CC, cingulated cortex; CP, caudate putamen; PB, paraterminal body; CP, caudate putamen; PC, parietal cortex; TC, temporal cortex; H, hippocampus; T, thalamus; HT, hypothalamus; AM, amygdala; SSC, stratum moleculare of the cerebellum; NCG, nucleus corporis geniculati; NR, nucleus rubber; SN, substantia nigra; NM, nucleus mammillaris; NC, deep nuclei of the cerebellum.