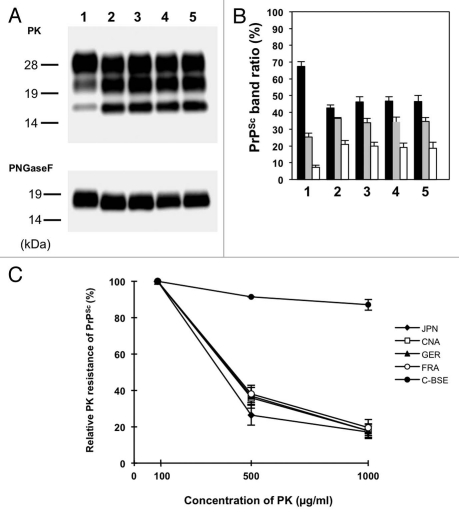
Figure 2.
Western blot analysis of proteinase K (PK)-digested prion protein (PrPcore) from the brain of L-type BSE isolate-affected TgBoPrP. (A) Lane 1, Classical-BSE; Lane 2, Japanese L-type BSE; Lane 3, Canadian L-type BSE; Lane 4, French L-type BSE; Lane 5, German L-type BSE. All the samples were digested with 50 µg/ml PK at 37°C for 1 h (upper part), and digested aliquots were treated with N-glycosidase F (PNGaseF), according to the manufacturer's instructions (bottom part). PrPcore was detected with mAb 6H4. Molecular markers are shown on the left (kDa). (B) The relative amounts of the diglycosylated (solid black bar), monoglycosylated (gray bar), and unglycosylated (clear bar) forms in the PrPcore from the brain of L-type BSE isolate-affected TgBoPrP. The lane numbers are as listed in (A). The results are presented as mean ± standard deviation from 5 experiments. (C) Relative PK resistance of PrPSc from L-type BSE isolate-affected TgBoPrP. The PrPSc concentration of the sample was adjusted using the western blot signal intensity. The samples were treated with various concentrations of PK (100–1,000 µg/mL). The results are presented as mean ± standard deviation from 3 experiments. PrPSc was detected with mAb 6H4. ◆, Japanese L-type BSE (JPN); □, Canadian L-type BSE (CAN); ▲, German L-type BSE (GER); ○, French L-type BSE (FRA); ●, Classical-BSE (C-BSE).