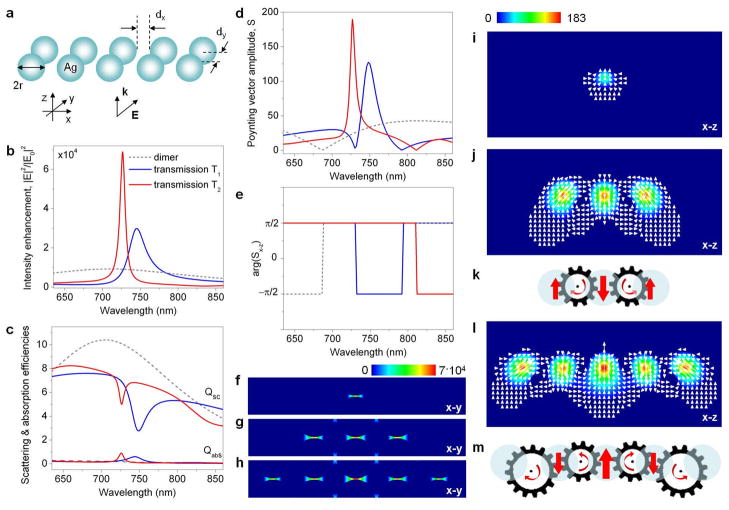
Fig. 9.
External plasmonic vortex nanogear transmissions. (a) Schematic of a linear chain of Ag nanoparticle dimers (r=50nm, dx=10nm, dy=3nm, ambient index n=1.33). Wavelength spectra of the electric field intensity enhancement in the gap of the central dimer (b), the far-field scattering and absorption efficiencies (c), the Poynting vector amplitude (d) and the phase of the Poynting vector in the x-z plane (e) in the gap of the central dimer of the nanostructures composed of three (solid blue lines) and five (solid red lines) nanodimers. The corresponding spectra of a single dimer are shown as dashed grey lines. The structures are illuminated by a plane wave with the electric field polarized along the dimers axes. Electric field intensity distribution in the gaps of a single dimer (f), three-dimer chain T1 (g), and five-dimer chain T2 (h). Poynting vector intensity distribution and powerflow through the gaps of the dimer (i), T1 (j) and T2 (l). Schematics of the VNTs generated in T1 (k) and T2 (m) at their resonant wavelengths. Light flux in each nanogear is looped between the particles.