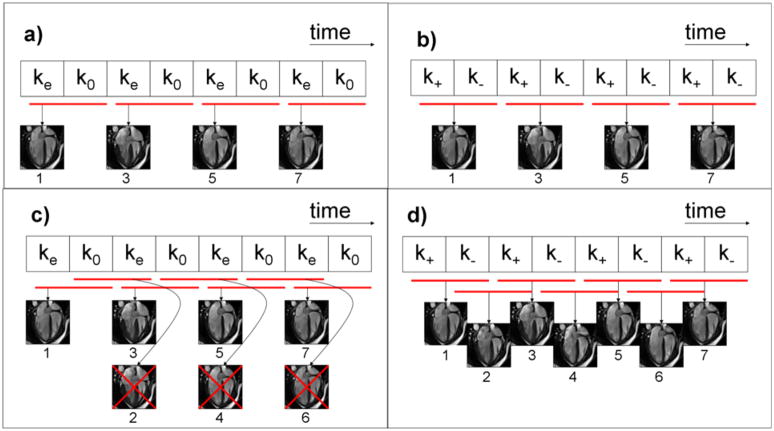
Figure 1.
The top two diagrams illustrate conventional one-sided (a) and two-sided (b) velocity encoding. The red bars in all diagrams show the data included in the reconstruction of each frame. One-sided velocity encoding (a) utilizes pairs of velocity encoded (ke) and velocity compensated (k0) k-space data. Two-sided encoding utilizes k-space data pairs with positive (k+) and negative (k−) velocity sensitivities (b). The proposed method of shared velocity encoding (SVE) image reconstruction is illustrated in (d). SVE cannot be combined with one-sided encoding as shown in (c) since image pairs sharing the same velocity encoded data (ke) would be redundant.