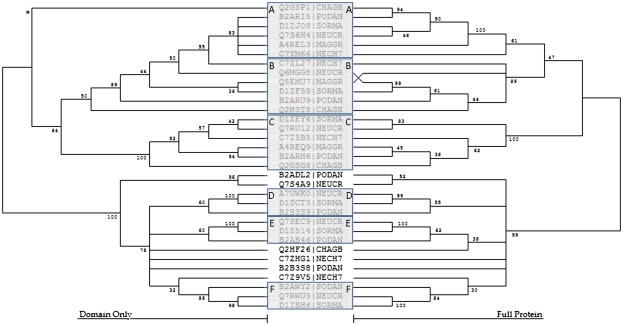
FIG. 3.
NJ analyses of F4 proteins from Sordariomycetes organisms. The NJ trees were inferred from the bHLH domain only and from the entire bHLH-containing protein sequence. The trees are displayed with corresponding bootstrap values where branches with a bootstrap of less than 30 have been collapsed. Six strongly supported F4 subclades have been noted, where subclades A–C contain one member from each Sordariomycetes organism and Groups D–F each have one member from Podospora anserina, Sodaria macrospora, and Neurospora crassa. * The Q2GSP1 bHLH domain has been determined to be highly divergent by 1) containing seven mismatches to the fungal consensus motif, 2) possessing an uncharacteristic amino acid at site 12 for an F4 protein (D), and 3) containing a simple sequence repeat through both the basic and Helix 2 regions (DDDDDD). The full Q2GSP1 sequence, however, is strongly supported in the A subclade, suggesting the highly divergent bHLH arose from either evolutionary pressure or sequencing errors.