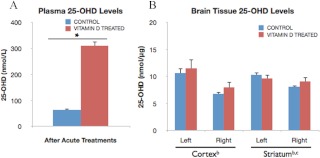
Fig. 6.
Levels of plasma and brain 25-OH vitamin D levels after vitamin D3 injections. Plasma and brain tissue was derived from control and vitamin D-treated female rats after five consecutive days of vehicle or vitamin D3 + vehicle ip injections, respectively. Samples were collected at 5 d after ischemia. A, Vitamin D treatments significantly increased circulating vitamin D, 25-OHD, levels (3.9-fold) as compared with levels in control rats injected with vehicle alone (*, P < 0.05). Bars represent mean ± sem. B, Brain 25-OHD levels, however, were not significantly affected by acute ip vitamin D3 treatments. There was a small but significant elevation of 25-OHD in ischemic tissues compared with nonischemic tissues. Additionally, in the striatum, 25-OHD levels were affected by an interaction of vitamin D treatment and ischemia, such that 25-OHD levels in the ischemic striatum were significantly higher in the control group compared with the vitamin D-treated animals. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA for hormone treatment and ischemia for each brain region; b, Main effect of ischemia; c, interaction effect of ischemia and hormone treatment. Bars represent mean ± sem; n = 4–5 in each group.