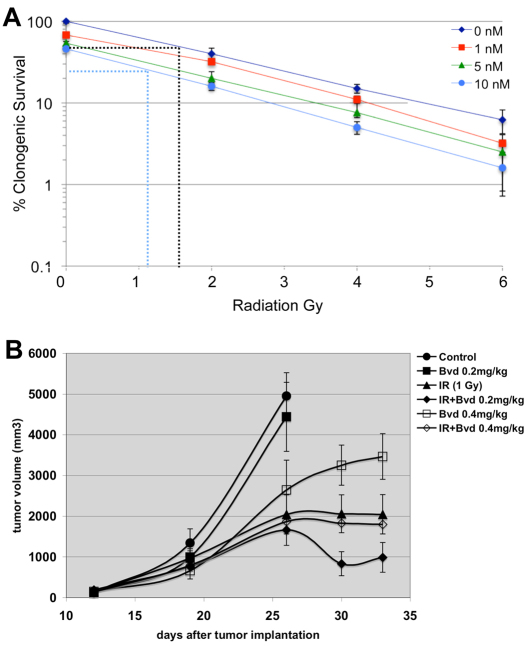
Fig. 3.
Bouvardin enhances the effect of IR on H157 cells in clonogenic assays and xenografts. (A) Clonogenic assays were used to confirm the effects of Bouvardin in combination with radiation in H157 cells. Cells were plated in six-well plates at 1000 cells per well. 24 hours later, various doses (1, 5 and 10 nM) of Bouvardin were added, with media alone as a control. 24 hours after the addition of Bouvardin, the cells were irradiated at 0, 2, 4 or 6 Gy. Colonies were allowed to form for 2 weeks and then counted. The results are shown as a percentage of control (no drug, no IR). Dotted lines illustrate the extrapolation to get IC50 for IR at 0 and 10 nM of drug (see Results). Error bar = ±1 s.e.m. (B) The effect of Bouvardin (Bvd) and radiation on H157 xenografts in athymic mice. Bouvardin treatment began when tumors had reached approximately 200 mm3. Bouvardin was administered intraperitonealy twice a week, and radiation was administered at 24 hours after each drug administration. At day 26, animals in the control and drug-only groups had tumors that were too large and had to be sacrificed. Treatment continued for the other four groups for one more week. The difference in tumor volume between the combination-treated group and radiation-only group was statistically significant at day 30 (P=0.0387 on day 30; unpaired two-tailed t-test). The difference in tumor volume between the combination-treated group and radiation-only group remains on day 33 but is less significant (P=0.0967; unpaired two-tailed t-test). n=10 per group. The data points indicate mean tumor volumes ± 1 s.e.m.