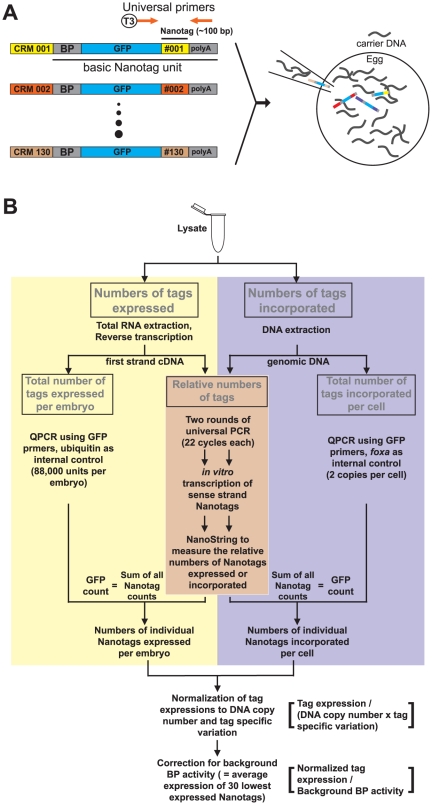
Figure 1. Architecture of Nanotags vectors and overview of workflow for the Nanotag-assisted cis-regulatory analysis.
(A) Architecture of Nanotag vectors. Each Nanotag vector is composed of a basal promoter (BP) derived from gatae [7], a GFP open reading frame, a unique ∼100 bp-long Nanotag sequence, and a core polyadenylation signal [8]. CRM::Nanotag constructs are built, pooled, and microinjected as described in Nam et al [1]. A pair of universal primers (orange coded) is designed for signal amplification. The forward universal primer contains T3 promoter sequence in its 5′-end for in vitro transcription of the sense strand of the entire pool of amplified Nanotags. Figure 1A is modified from Nam et al [1]. (B) Overview of the Nanotag-assisted cis-regulatory analysis. Two parallel protocols respectively for measuring the numbers of individual tags expressed (left panel) and those of incorporated (right panel) are shown. While QPCR is used to measure the total number of tags expressed per embryo from first strand cDNA or the total number of tags incorporated per cell from genomic DNA, the NanoString was used to measure the relative numbers of individual tags from amplified cDNA or amplified genomic DNA with much improved sensitivity. The numbers of individual tags incorporated per embryo are estimated by comparing results from QPCR and NanoString analyses. The level of tags expressed is corrected for DNA copy number, tag specific variations, and background BP activity specific to each sample.