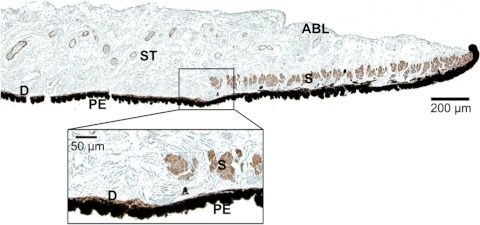
Figure 4.
Histologic image of the pupillary and midperipheral portions of the porcine iris. Monoclonal anti-human α-smooth muscle actin stain was used to differentiate the muscular tissues, including the sphincter (S) and dilator (D). The pigment epithelium anterior border layer (ABL); stroma (ST), which is a loosely arranged collagen network; and another thick layer of pigment epithelial (PE) cells on the posterior surface of the iris is also identifiable. Magnification of the midperiphery regions illustrates that dilator muscle lies on the posterior iris surface and is very thin compared with the sphincter muscle.