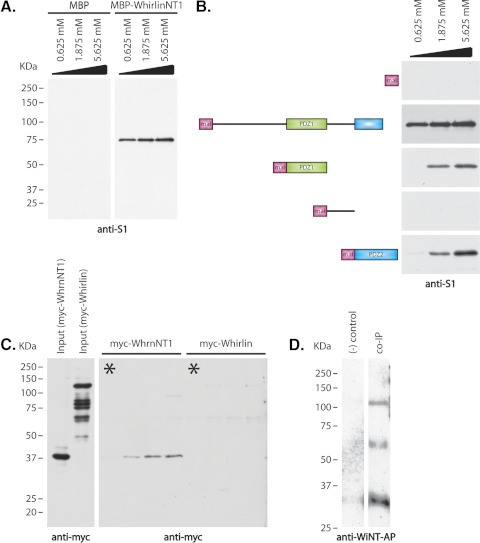
Figure 3.
Confirmation and analysis of RpgrORF15–whirlin interaction. (A) Extracts of transfected HEK293 cells expressing a 75-kDa RpgrORF15 isoform were incubated with immobilized MBP-tagged whirlinNT1 isoform (0.625 mM, 1.875 mM, and 5.625 mM) or MBP alone (0.625 mM, 1.875 mM, and 5.625 mM). Bound Rpgr was analyzed by immunoblot with the S1 antibody to identify Rpgr isoforms. (B) Schematic representation of the various whirlin constructs used and immunoblot analysis of pull-down assays used to identify RpgrORF15 binding domain. From top: MBP protein (negative control); MBP-whirlinNT1 isoform (positive control); MBP-whirlin PDZ1 domain; MBP-whirlin inter PDZ1/PDZ2 domain; MBP-whirlin PDZ2 domain. Increasing molar concentrations (0.625 mM, 1.875 mM, and 5.625 mM) of each fusion protein were immobilized on amylose resin and were incubated with equal amounts of HEK293 cells lysate expressing a 75-kDa RpgrORF15 isoform. (C) Comparison of RpgrORF15 interaction with the whirlinNT1 isoform and the long whirlin isoform. Left: myc-tagged whirlinNT1 and whirlin long isoforms from transfected HEK293 cells. The smaller bands in the whirlin long isoform lane are degraded protein detected by the myc antibody. Right: immunoblot of binding assay. Increasing amounts of MBP-ORF15 fusion protein were incubated with fixed amounts of either the myc-tagged whirlin NT1 or the myc-tagged long whirlin isoform. Asterisk: negative control in which MBP was substituted at the highest molar concentration of MBP-ORF15 fusion protein. (D) Immunoblot of coimmunoprecipitation to confirm RpgrORF15–whirlin interaction in vivo. Rpgr was immunoprecipitated from Rpgrip knockout retinal homogenate using anti–S1 antibody. Bound protein was analyzed by immunoblot using alkaline phosphatase–tagged anti–WiNT antibody. Left: negative control of immunoprecipitation using preinoculated antisera in place of anti–S1 antibody. Right: immunoprecipitation using anti–S1 antibody.