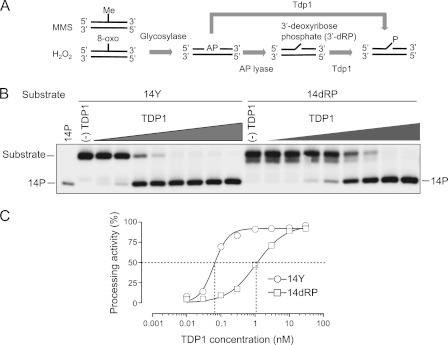
FIGURE 6.
Involvement of Tdp1 for repair of abasic (AP) sites. A, scheme for the conversion of MMS- and H2O2-induced DNA damage into the substrates for Tdp1. DNA adducts like methylated base and 8-oxoguanine (8-oxo) are converted into AP sites by DNA glycosylase. In one way, Tdp1 cleaves the AP site, directly generating the 3′-phosphate end. In the other way, the AP site turns out to be a single strand break with a 3′-dRP end after hydrolysis by AP lyase. Tdp1 cleaves the 3′-dRP, generating the 3′-phosphate end. B, processing activity of recombinant human TDP1 on the 14-nt 3′-phosphotyrosyl substrate (14Y) and the 14-nt 3′-dRP substrate (14dRP). Each substrate was incubated with serial dilutions (1:3) of TDP1 at 25 °C for 30 min with the highest concentration starting at 30 nm. The 14-nt 3′-phosphate (14P) was used as a marker. A gel representative of consistent results in independent experiments is shown. C, quantification of TDP1 processing activity for each substrate from B. EC50 values (the half-maximal effective concentration) for 14Y and 14dRP are 0.062 and 1.078 nm, respectively.