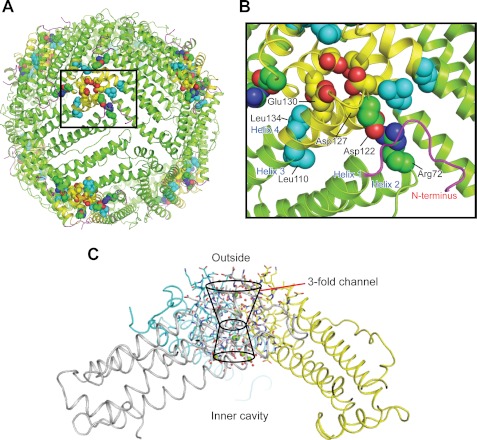
FIGURE 1.
Conserved interactions rigidify the ion entry and exit channels at the 3-fold symmetry axes of ferritin protein cages. A, the ferritin protein cage of a eukaryotic ferritin (24 subunits), the frog M ferritin model (PDB code 3KA3). Boxed region, the ion entry and exit channel. B, space-filling representations of selected residues important in ferritin ion channel function. C, a single ferritin ion channel at the junction of three subunits. The cross-section of helix 3-loop-helix 4 from one of the three subunits that form the Fe2+ entry and exit channels is shown with residues involved in ion channel activity. Asp-127 and Glu-130 affect Fe2+ entry in solution studies (4, 52, 53). Arg-72, Leu-110, Asp-122, and Leu-134 affect Fe2+ exit in solution studies (11, 12, 18). Yellow, helix-turn-helix of one of the three subunits; green, the major section of the four-helix bundle that contains the active site and nucleation channel; magenta, the N-terminal peptide.