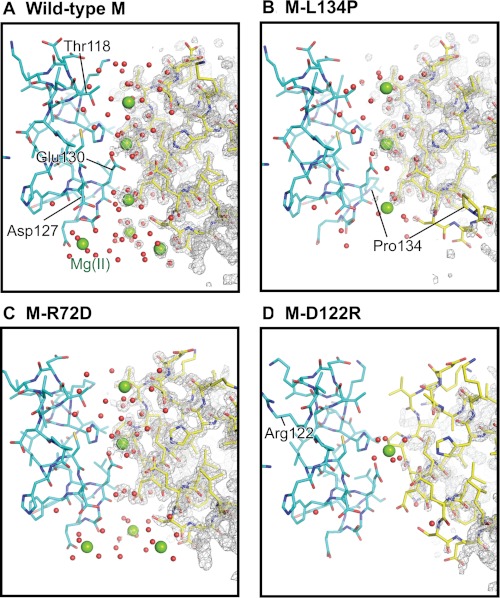
FIGURE 6.
Effects of changing conserved ferritin Fe2+ exit residues on channel ion binding. There are four Mg2+ sites per ion channel (sites A–D, from outside to inside (supplemental Table S1)). A, wild type; full occupancy at sites A–D. B, M-L134P; zero occupancy at site D; partial occupancy at sites A, C, and D; and full occupancy at site B, the channel constriction. C, M-R72D (N-terminal gate “open”); similar to wild-type ferritin, except there is no binding at site C. D, M-D122R; zero occupancy at site A, C, or D and full occupancy at site B, the channel constriction. The changes in Mg2+ ion occupancies track channel main-chain flexibility (Fig. 2) and effects on Fe2+ exit in mineralized ferritin (Fig. 3). Green spheres, hydrated Mg2+; red dots, ordered water; gray mesh, 2Fo − Fc electron density.