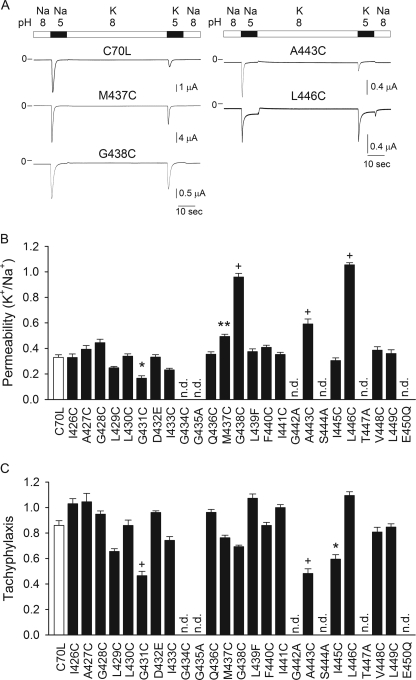
FIGURE 4.
Contribution of residues in TM2 segment to ion selectivity. A, representative recordings of proton-activated currents obtained from oocytes expressing ASIC1a mutants. Whole-cell currents were elicited by a change in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 5.0 with Na+ or K+ as the main permeable cation. B, K+/Na+ permeability of mutant ASIC1a channels. ASIC1a mutants have a C-terminal HA epitope tag. Whole-cell currents were elicited by a change in extracellular pH from 8.0 to 5.0. The peak current evoked by extracellular acidification with K+ as the main permeable cation was normalized to the peak current evoked by extracellular acidification with Na+ as the main permeable cation. Currents were normalized by tachyphylaxis (see below). C, tachyphylaxis of ASIC1a mutants. The response to repetitive acid stimulations was determined with Na+ as the main permeable cation. ASIC1a mutants were activated by a change in extracellular pH from 8 to 5. Tachyphylaxis is defined as the ratio of the peak currents of two consecutive activations elicited by extracellular acidification (second peak current relative to the first peak current). Statistically significant differences with the control (C70L) are indicated as *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, and + p < 0.001 (n = 10–43) (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test). n.d., not detectable.