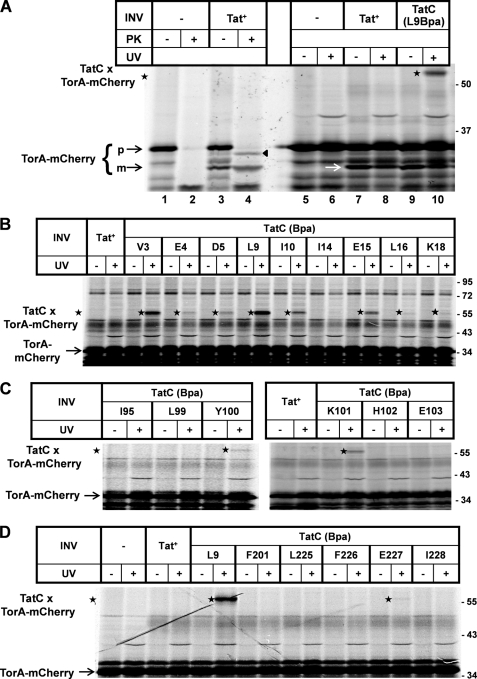
FIGURE 2.
Cross-links between TatC and the model RR precursor TorA-mCherry. A, TorA-mCherry was synthesized by in vitro transcription/translation in the presence of [35S]methionine/cysteine. Radiolabeled translation products were separated by SDS-PAGE and are visualized by phosphorimaging. Numbers to the right indicate the molecular masses in kDa of marker proteins. Where indicated, INV were present during synthesis. INV were prepared from an E. coli wild-type strain overexpressing TatABC (Tat+) or a strain expressing in the same genetic background a TatC variant, in which the leucine at position 9 had been replaced by Bpa (L9Bpa). Indicated are the precursor of TorA-mCherry (p) and the mature form (m) obtained by INV-mediated signal sequence cleavage. Besides processing, translocation of TorA-mCherry into the lumen of the INV is also indicated by the acquirement of PK resistance of the precursor (black triangle) and the mature form. Only in the presence of TatC(L9Bpa)-INV did irradiation of the samples with UV-light (UV) give rise to an adduct (star) that by size corresponds to a 1:1 complex between TatC and TorA-mCherry. B, as in A except that cross-linking was performed with different INV each one carrying a Bpa substitution at the indicated positions within the N terminus of TatC. C, as in B using Bpa variants of the first cytosolic loop of TatC. D, as before comparing the L9Bpa and E227Bpa variants of TatC, the latter being located in the sixth TM of TatC.