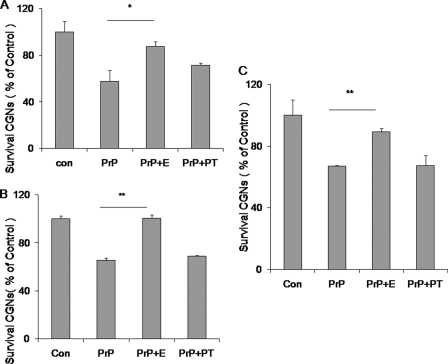
FIGURE 6.
Effects of PrP-AA on wild type or mutant PrP106–126 induced neurotoxicity. Exposure of rat CGN to 50 μm PrP106–126(A117V or wild type) fibril resulted in a reduction of neuronal survival during a 3 day incubation period. Purified PrP-AA (0.07 μm) significantly attenuated PrP106–126(A117V) fibril-induced neuronal death. A, PrP106–126(A117V) peptides (50 μm) were incubated with PrP-AA (0.07 μm) before being exposed to neurons. B, preformed PrP106–126(A117V) fibrils were incubated with PrP-AA (0.07 μm) before being exposed to neurons. C, preformed wild-type PrP106–126(117A) fibrils were incubated with PrP-AA (0.07 μm) before exposed to neurons. Cell viability was determined by staining neurons with fluorescein diacetate/propidium iodide. The data represent the mean ± S.D. of triplicate determinations from a representative experiment repeated at least three times with similar results (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001, compared with PrP106–126 only, one-way ANOVA). Con, untreated cultures; PrP, PrP106–126 (A117V or wild type) peptides; E, PrP-AA; PT, pass-through IgG depleted of PrP-AA.