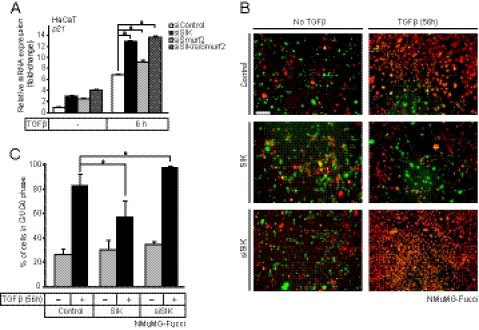
FIGURE 6.
Endogenous SIK regulates epithelial growth arrest by TGFβ signaling. A, quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis measuring the effects of SIK, Smurf2, and combined SIK/Smurf2 siRNA knockdown on the cell cycle inhibitor gene p21 mRNA levels in HaCaT cells with or without (−) stimulation with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 6 h. QRT-PCR analysis was performed and are presented as in Fig. 1. Asterisks indicate significant differences determined by Student's t test with significance at p < 0.01. B, shown is live fluorescence microscopy of mammary epithelial NMuMG-Fucci cells transiently transfected with control scrambled siRNA followed by infection with control Ad-LacZ virus (control, upper panels), transiently transfected with specific siRNA targeting SIK (siSIK, bottom panels) or transiently infected with an adenoviral vector expressing SIK (middle panels). The cells were treated with vehicle (no TGFβ) or 5 ng/ml TGFβ1 for 56 h before photography. A bar indicates 20 μm. C, shown is quantitative analysis of the cell cycle from experiments such as that shown in panel B. The number of red cells (G1/G0 phase) were counted in duplicate photos from two independent experiments from each experimental condition and are plotted as % relative to the total number of cells. Statistical significance between conditions is shown with a asterisk that indicates p < 0.05.