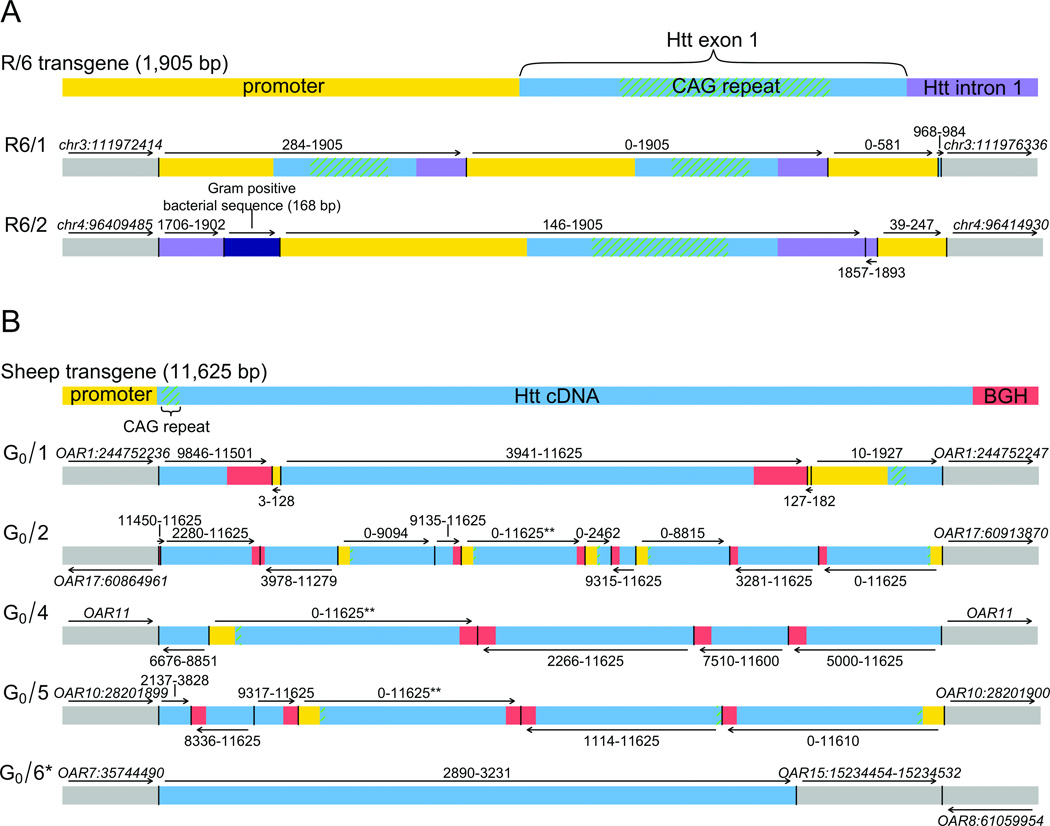
Figure 3. Complex rearrangements in transgenic animals.
Results from sequencing of two transgenic mice (A) and five transgenic sheep (B). Each transgene prior to pronuclear injection is provided in the first line and resultant transgene integration site and internal structure is shown below for each animal. Genomic integration sites are given by the gray lines flanking the transgene and the most parsimonious transgene structure is shown (R6/1,2 mice and G0/1,2,4,5,6 sheep). The fragment injected into the R6 lines (1,905 bp) comprised the human HTT promotor, exon 1 (~130 CAG repeats), and 264 bp of human intron 1. The fragment injected into the sheep (11,625 bp) included the human HTT promoter and cDNA (69 CAG repeats), followed by exon 4, intron 4, and exon 5 of the bovine growth hormone (BGH) gene. Arrows represent strand orientation. *This transgene was fragmented and inserted into multiple chromosomal locations; one of the small fragments and resultant complex rearrangements of the host genome involving three independent chromosomes is shown here (see also Fig. 1, Supplementary Fig. 1). **Head-to-tail junctions and read depth analyses indicate multiple copies of the segment, however the precise number of duplications could not be determined. Mouse positions are mm9 and sheep positions are OAR2.