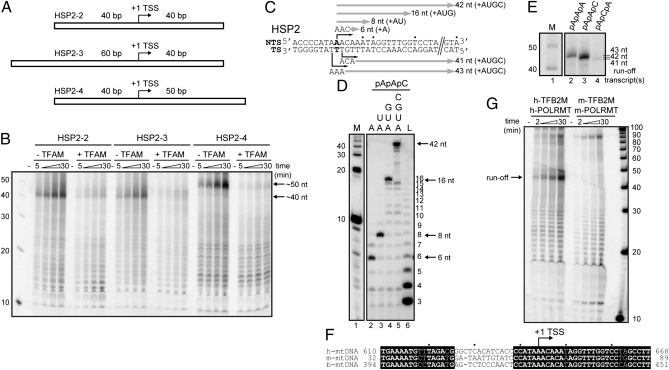
Fig. 2.
Specificity of HSP2 transcription in vitro. (A) HSP2 transcription templates designed to assess the specificity of initiation. (B) Runoff transcription from the templates shown in A by POLRMT-TFB2M in the absence or presence of TFAM. (C) Sequence surrounding HSP2; shown are the expected start sites and sizes of RNA transcripts when using pApApC, pApApA, or pApCpA trinucleotide primer for initiation with the indicated nucleotide(s). (D) Transcription by POLRMT-TFB2M from the HSP2-1 template in the presence of pApApC and the indicated nucleotide(s). (E) Runoff transcription from the HSP2-1 template in the presence of pApApA, pApApC, or pApCpA trinucleotide primer and all four nucleotides. (F) Alignment of human HSP2 with corresponding mouse and bovine sequences reveals a region of high interspecies differences from −18 to −6. (G) Mouse POLRMT-TFB2M fails to produce a promoter-specific runoff transcript from human HSP2 indicating specificity of human POLRMT-TFB2M.