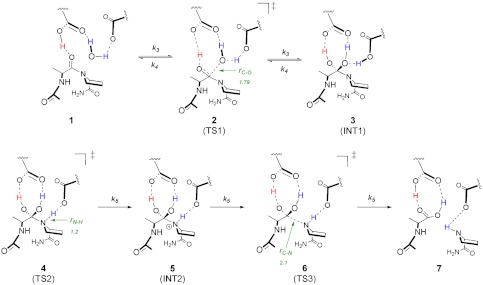
Fig. 1.
Chemical mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by HIV-1 protease. Structures along the pathway are indicated as follows: (1) enzyme-substrate complex; (2) water attack TS; (3) tetrahedral gem-diol intermediate; (4) proline N-protonation TS; (5) protonated amide intermediate; (6) cleavage of scissile C-N bond TS; and (7) enzyme-product complex. For transition structure 2, the r(C-O) bond distance is defined as the distance between the oxygen of the attacking water and the carbonyl carbon of the peptide. For transition structure 4, the r(N-H) is defined as the bond distance between the nitrogen on the proline, and the proton on the catalytic aspartate and r(H-O) is defined as the bond distance between the oxygen and proton on the catalytic aspartate. Finally, in transition structure 6, r(C-N) is the bond distance of the scissile bond of the peptide.