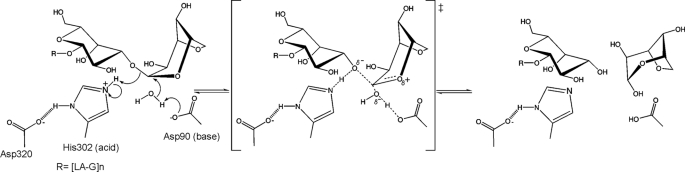
FIGURE 6.
Proposed mechanism of neoagaro-oligosaccharide hydrolysis by GH117 enzymes. The reaction occurs via a single displacement mechanism showing the oxocarbenium-like transition state. His302 acts as the general acid to facilitate cleavage of the glycosidic bond, whereas Asp90 acts as a general base to activate a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the C1 carbon of the 3,6-anydro-l-galactose.