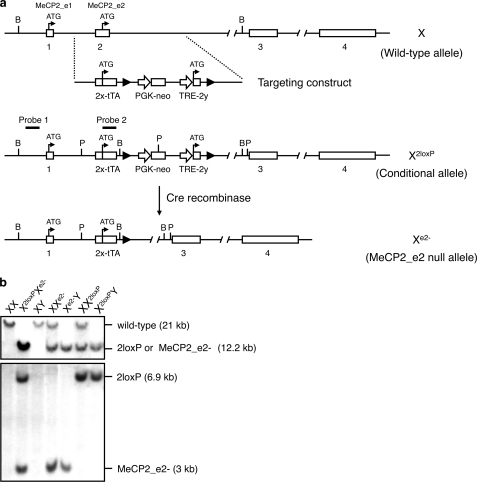
FIGURE 1.
Generation of MeCP2_e2-deficient mice. a, strategy for selective targeting of MeCP2_e2. Transcription start sites for MeCP2_e2 and MeCP2_e1 before and after exon 2 disruption are shown. loxP sites are denoted as filled triangles. Relative location of probes for Southern hybridization, and positions of restriction enzymes BamHI (B) and PvuII (P) are indicated. Crossing of MeCP2_e2 conditional mice with Nestin-Cre deleter mice results in the excision of the transcriptional start site of MeCP2_e2 and the creation of the MeCP2_e2 null allele, not only in neuronal cells but also in the germ line. Note that the transcriptional start of MeCP2_e1 remains intact after disruption of the MeCP2 locus. b, MeCP2_e2 wild-type and mutant alleles as differentiated by two sets of Southern hybridization. For the first screening (top), genomic DNA was digested with BamHI and probed to visualize the presence of the targeted MeCP2 locus containing the exon 2x-tTA sequence. In the second screening (bottom), PvuI-digested genomic DNA was probed to differentiate between the conditional (X2loxP) and null (Xe2−) alleles. Approximate band sizes are indicated in parentheses.