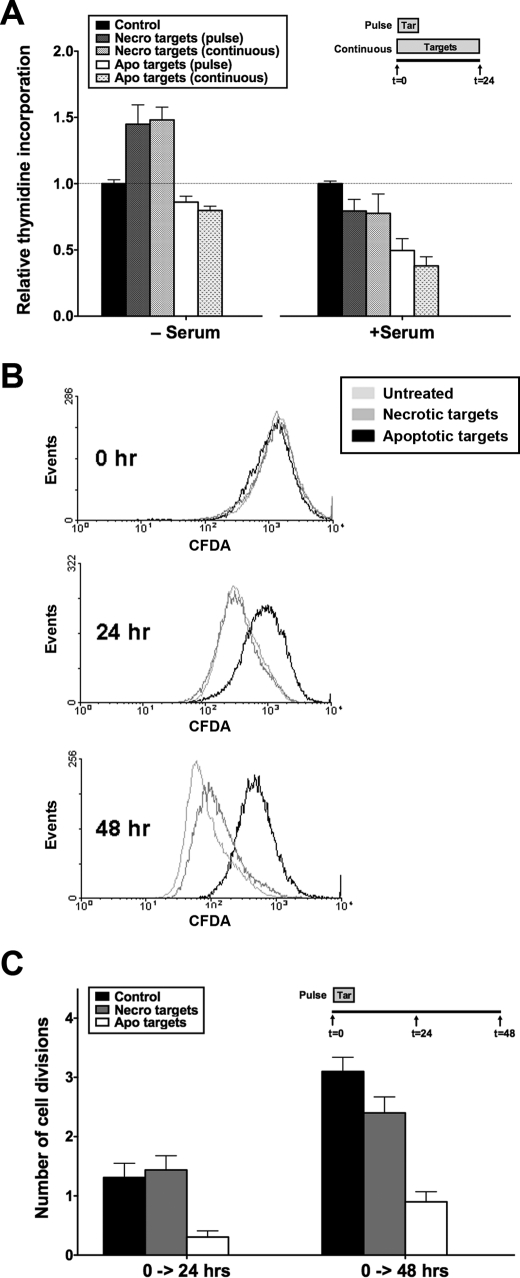
FIGURE 2.
Apoptotic targets decrease viability of BU.MPT responder cells through inhibition of responder cell proliferation. A, serum-starved BU.MPT responder cells in the presence or absence of FBS (10%, v/v) were exposed to apoptotic (Apo) or necrotic (Necro) targets at a target/responder cell ratio of 10:1 either continuously for 24 h or as a single 2-h pulse, as depicted in the inset. The source of apoptotic targets was actinomycin D-treated DO11.10 cells. As a measure of proliferation, [3H]thymidine incorporation was determined during the final 2 h of a 24-h incubation. Counts per minute (cpm) were normalized against those for responder cells not exposed to targets as represented by the dotted line at relative thymidine incorporation equal to 1.0. Each data point in the graph represents the mean and S.E. from a minimum of three separate experiments. Absolute cpm for responders unexposed to targets in the absence and presence of serum were 5376 ± 830 and 8061 ± 632, respectively. p < 0.05, necrotic targets (pulse) and necrotic targets (continuous) versus control in the absence of serum; p < 0.01, apoptotic targets (pulse) and apoptotic targets (continuous) versus control in the presence of serum. B, BU.MPT responder cells (prelabeled with CFDA-SE) were exposed to apoptotic (Apo) or necrotic (Necro) targets at a target/responder cell ratio of 10:1 for 2 h. The source of apoptotic targets was actinomycin D-treated DO11.10 cells. Proliferation of BU.MPT responders was assessed at 0, 24, or 48 h after target exposure by cytofluorimetric analysis of the reduction in CFDA-SE staining. C, the graph depicts the mean and S.E. from three separate cytofluorimetric analyses of the cumulative number of cell divisions within the indicated time intervals as determined by Equation 1 given under “Experimental Procedures.” p < 0.01, apoptotic targets versus control, 0–24 h; p < 0.001, apoptotic targets versus control, 0–48 h; p = not significant, necrotic targets versus control, 0–24 and 0–48 h. Tar, target(s). Error bars (A and C) denote S.E.