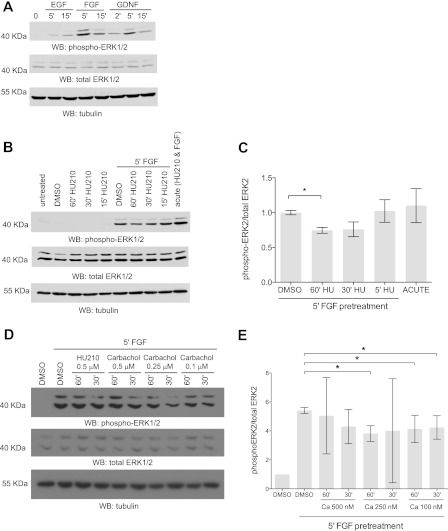
FIGURE 7.
Active Gαo signaling attenuates FGF signaling. A, Neuro-2A cells express functional FGF receptors. Neuro-2A cells were serum-starved overnight and then treated with 50 ng/ml EGF, 20 ng/ml FGF, or 20 ng/ml glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) for various periods of time (0, 2, 5, or 15 min). Western blots (WB) were performed with monoclonal anti-dual phospho-p44/42 MAPK (top panel), polyclonal anti-dual total p44/42 MAPK (middle panel), and anti-tubulin antibodies (bottom panel). Representative immunoblots from one of three experiments are shown. B, CB1R prestimulation decreases FGF signaling. Neuro-2A cells were serum-starved overnight and pretreated with 500 nm HU-210 at different time points (15, 30, and 60 min) followed by stimulation with FGF for 5 min. Total cell lysate was resolved by immunoblotted with monoclonal anti-dual phospho-p44/42 ERK1/2 (top panel), polyclonal anti-dual total p44/42 ERK1/2 (middle panel), and anti-tubulin antibody (bottom panel). Representative immunoblots from one of three independent experiments are shown. C, corresponding densitometric data for the average of three independent experiments. Error bars indicate S.E. D, muscarinic receptor prestimulation decreases FGF signaling. Neuro-2A cells were serum-starved overnight and pretreated with different concentrations of carbachol (500, 250, or 100 nm) at different time points (30 and 60 min) followed by stimulation with FGF for 5 min. Total cell lysate was immunoblotted with monoclonal anti-dual phospho-p44/42 ERK1/2 (top panel), polyclonal anti-dual total p44/42 ERK1/2 (middle panel), and anti-β tubulin antibody (bottom panel). Representative immunoblots from one of three independent experiments are shown. E, corresponding densitometric data for the average of three independent carbachol experiments. *, p < 0.05. Error bars indicate S.E.