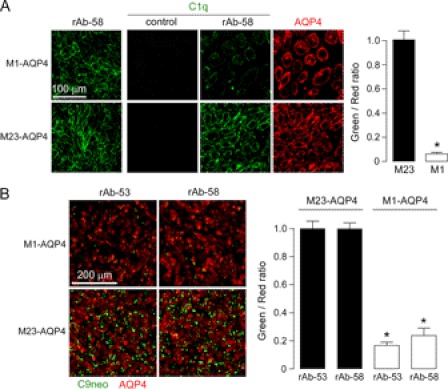
FIGURE 7.
Greatly reduced C1q binding to NMO-IgG accounts for resistance of M1-AQP4-expressing cells to CDC. A, left, staining of M1- and M23-AQP4 in CHO-K1 cells with 40 μg/ml NMO rAb-58. Center panels, C1q staining. Cells were incubated with 40 μg/ml rAb-58 (or control rAb) and 120 μg/ml purified recombinant C1q for 30 min, fixed, and stained with FITC-conjugated anti-C1q antibody. AQP4 was stained red with anti-AQP4 antibody. Right, green-to-red fluorescence ratio (S.E., n = 4, *, p < 0.001). B, C9neo immunostaining. Left, cells were incubated with 20 μg/ml rAb-53 or rAb-58 and 2% complement for 30 min, fixed, and stained with anti-C9neo antibody and green fluorescent secondary antibody. AQP4 was stained red. Right, green-to-red fluorescence ratio (S.E., n = 4, *, p < 0.001).