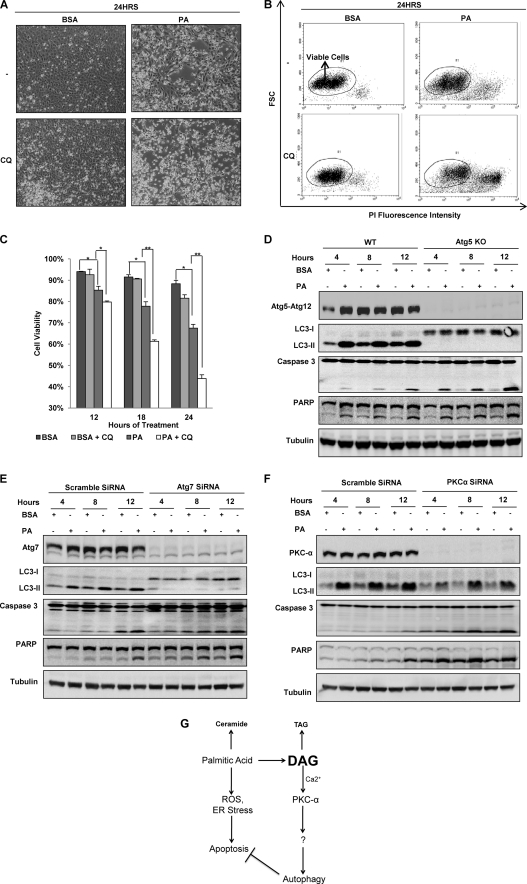
FIGURE 7.
Autophagy acts as a cell survival mechanism against lipotoxicity caused by PA. A, cell morphology was observed under a phase contrast microscopy (×200) of MEFs treated with either BSA control or PA (0.25 mm) for 24 h with or without the presence of CQ (10 μm). B, shown are representative dot-plots of flow cytometry data of the PI exclusion test. MEFs were treated as described in panel A. C, quantification of the cell viability data from panel B is shown. Data were presented as the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, Student's t test). D, WT and Atg5 KO MEFs were treated with either BSA control or PA (0.25 mm) for the indicated time points. PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. E, Atg7 was knocked down with Atg7 siRNA, and the cells were treated with either BSA control or PA (0.25 mm) for the indicated time points. F, PKC-α was knocked down with PKC-α siRNA, and the cells were treated with either BSA control or PA (0.25 mm) for the indicated time points. G, shown is a summary of the proposed signaling pathways involved in PA-mediated autophagy and its pro-survival role in PA-induced apoptosis and lipotoxicity. ROS, reactive oxygen species.