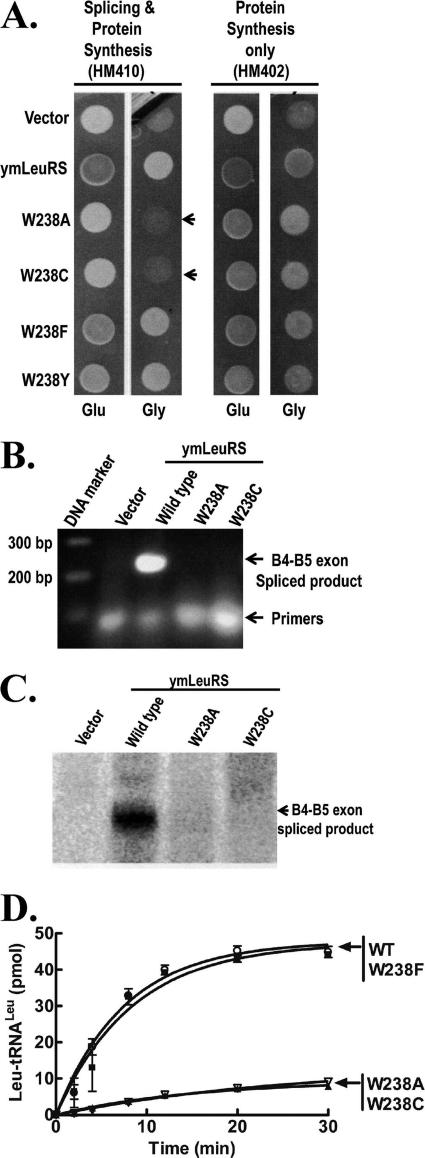
FIGURE 6.
The Trp-238 mutation in the WIG peptide abolishes splicing but maintains sufficient aminoacylation activity. A, complementation assays used yeast null strains HM410 and HM402 and is indicated by darker colonies grown on glucose (Glu) media and by growth on glycerol (Gly) media. Arrows highlight colonies expressing full-length W238A and W238C mutant ymLeuRSs support growth of HM402 but not of HM410 on Gly media. Both strains were transformed with the parent vector pQB153T or with plasmids expressing the full-length wild type (pymLRST) or W238A (pMPW238A), W238C (pMPW238C), W238F (pMPW238F), and W238Y (pMPW238Y) mutant ymLeuRSs. B, RNA amplification via RT-PCR of total cellular RNA from yeast null strain HM410 expressing full-length wild type and Trp-238 mutant ymLRSs yielded a 250 base pair (bp) amplified product representing the B4-B5 ligated exon product on a 1% agarose gel. C, shown is a Northern blot of 100 μg of total cellular RNA isolated from HM410 yeast cells expressing full-length wild type and Trp-238 mutant ymLeuRSs. Hybridization was carried out with a 32P-labeled B4-B5 exon junction probe. D, in vitro aminoacylation activity of full-length wild type and Trp-238 mutant LeuRS is shown. Reactions included 4 μm transcribed ymtRNALeu, 1 μm enzyme, and 21 μm [3H]leucine (150 μCi/ml) and were initiated with 4 mm ATP. ■, wild type; ▾, W238A; △, W238C; ○, W238F. Error bars for each time point result from each reaction repeated in triplicate.