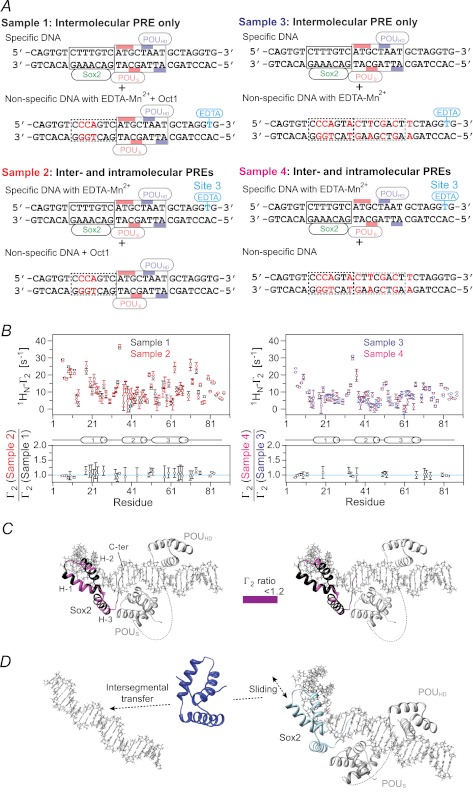
FIGURE 8.
Intramolecular versus intermolecular translocation of Sox2 in the context of the Oct1·Sox2·Hoxb1-DNA ternary complex. A, DNA samples comprise an equimixture of specific and nonspecific 29-bp DNA duplexes. In samples 1 and 3, the specific DNA duplex is unlabeled, and the nonspecific DNA duplex bears the paramagnetic label with (sample 1) or without (sample 3) retention of the Oct1-binding site. In samples 2 and 4, the nonspecific DNA duplex with (sample 2) or without (sample 4) the Oct1-binding site is unlabeled, and the specific DNA duplex is paramagnetically labeled 3′ of the POUHD site (denoted as site 3 using the notation in Fig. 7A). The PRE effects observed for samples 1 and 3 arise entirely from intermolecular translocation of Sox2 from the specific duplex to the nonspecific duplex and back again for observation, whereas those for samples 2 and 4 arise from both intra- and intermolecular translocation processes. The concentrations of 2H/15N-Sox2, Oct1, specific DNA, and nonspecific DNA are 0.40, 0.90, 0.45, and 0.45 mm, respectively, for samples 1 and 2; for samples 3 and 4, the concentration of Oct1 is reduced to 0.45 mm because the nonspecific DNA no longer contains the specific Oct1 site. The concentrations of Oct1 were chosen to ensure that all specific Oct1-binding sites are occupied. B, intermolecular PRE profiles at 150 mm NaCl (top panels), with intermolecular PREs from samples 1 and 2 (left) and samples 3 and 4 (right) shown as black, red, blue, and magenta circles, respectively (error bars, S.D.). Bottom panels, ratio of PRE rates for sample 2 to sample 1 (left) and for sample 4 to sample 3 (right) for residues with 1HN-Γ2 rates of >10 s−1. For Γ2(sample 2 or 4)/Γ2(sample 1 or 3) ∼ 1, the PRE effects arise predominantly from intermolecular translocation; Γ2(sample 2 or 4)/Γ2(sample 1 or 3) ratios larger than 1 indicate contributions from both intra- and intermolecular translocation processes, where the contribution from the latter is provided by the PRE profile for sample 1 or 3. C, Γ2 ratios shown in B mapped onto the structure of the specific Oct1·Sox2·Hoxb1-DNA ternary complex (23). D, model for the predominant translocation processes involving Sox2 in the context of the specific Oct1·Sox2·Hoxb1-DNA ternary complex.