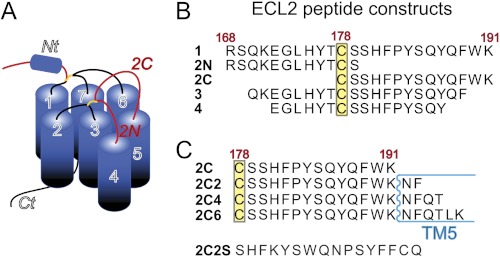
FIGURE 1.
Schematic of CCR5 and ECL2 peptide constructs used in this study. A, the region of CCR5 corresponding to ECL2 is shown in red, and the helical N terminus is labeled and shown as a cylinder. B, amino acid sequences of the ECL2 peptide constructs predicted to reside in the extracellular region of ECL2. C, C-terminal ECL2 peptide sequences that contain additional residues predicted to reside in TM5.