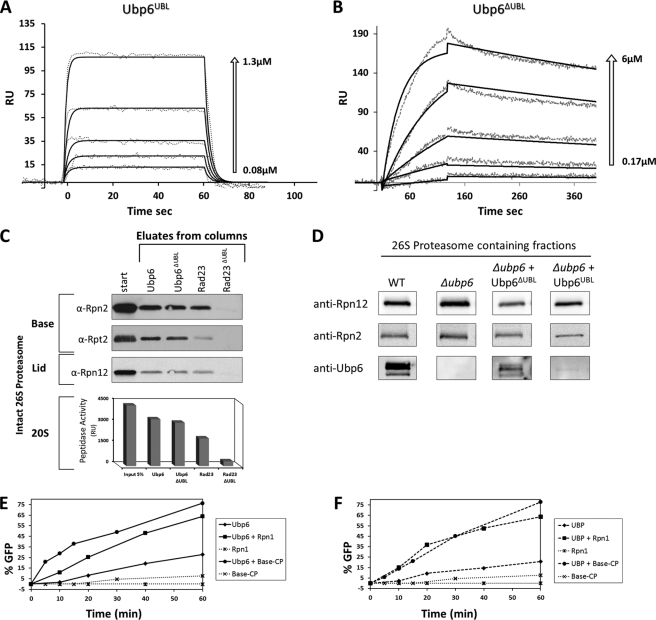
FIGURE 3.
Two-step proteasome incorporation of Ubp6. A and B, SPR sensograms of Ubp6UBL and Ubp6ΔUBL binding kinetics to Rpn1. The response data for binding and dissociation (dotted lines) are shown for a series of concentrations (arrows). Values of best fit parameters to a single bimolecular interaction model (solid lines) are summarized in Table 3. RU, response units. C, immobilized Ubp6 and Rad23 lacking their UBL domains (Ubp6ΔUBL and Rad23ΔUBL) were tested for binding to 26 S proteasome-purified free of all UDPs or other transient proteasome-interacting proteins. Association of full-length Ubp6 and Rad23 is included as positive control. Eluate from each column was tested for proteasome activity (20 S CP) as well as immunoblotted (IB) for presence of 19 S subunits from the Base and Lid subcomplexes. D, truncated Ubp6-expressing strains were molecular weight-fractionated, and proteins copurifying with peak of proteasome activity were identified by immunoblotting. E, potency of Ubp6 to remove ubiquitin from Ub-GFP was monitored over 60 min, and % reaction progression was plotted over time (diamonds). The reaction was repeated in presence of equimolar Rpn1 (squares) or purified base-CP (lidless) proteasome lacking both endogenous Ubp6 and Rpn11 (circles). Neither Rpn1 (star) nor base-CP alone (×) exhibit deubiquitination activity in the absence of added Ubp6 (dotted lines). F, experiment similar to E but for truncated Ubp6ΔUBL. Ubp6 activation is not dependent on UBL.