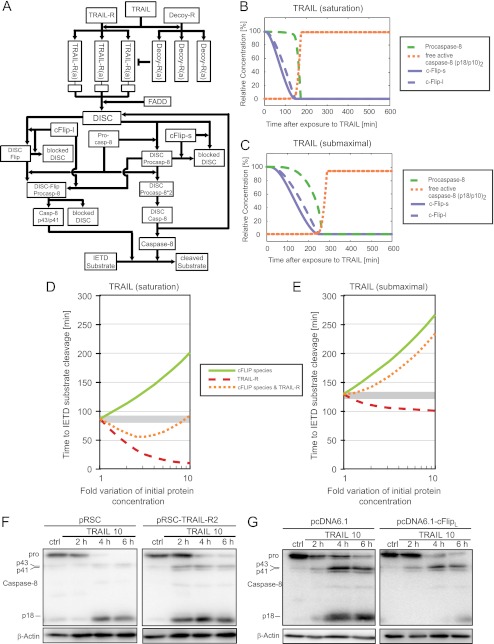
FIGURE 2.
Systems modeling and sensitivity analysis of the apoptotic TRAIL signaling network in HeLa cervical cancer cells. A, the biochemical reactions depicted in the reaction network were mathematically modeled using ordinary differential equations. This allowed to calculate signal transduction kinetics and to perform analyses on the systems responsiveness to perturbations. In particular, the model was used to evaluate how the time required to translate TRAIL exposure into caspase-8 activation is influenced by single or combined perturbations in cFLIP and TRAIL-R levels. A detailed description of the model implementation is provided as supplemental information 1. B and C, signaling kinetics of TRAIL induced apoptosis initiation in response to saturating (B) or submaximal (C) TRAIL doses, respectively. D and E, response sensitivity of the signaling network when stimulated with saturating (D) or submaximal (E) TRAIL doses, respectively. Shown are the times required to initiate the cleavage of caspase-8 substrates following single perturbations in the amounts of TRAIL receptors and cFLIP species or parallel increases in both TRAIL receptors and cFLIP species. F, whole cell extracts of HeLa cells transfected with empty vector or a TRAIL-R2 expression plasmid were analyzed for procaspase-8 processing. Cells were treated with 10 ng/ml TRAIL plus 1 μg/ml CHX for the indicated times. β-Actin served as loading control. G, as in F, empty vector-transfected or cFLIPL overexpressing HeLa cells were analyzed for procaspase-8 processing.