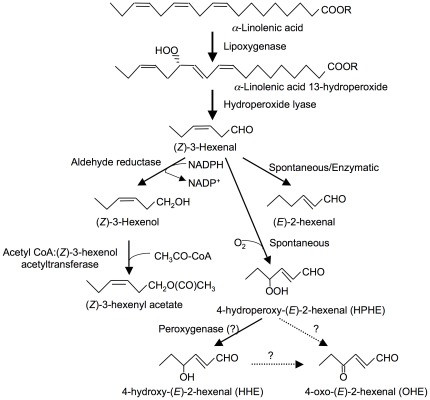
Figure 1. Biochemical pathway for the formation of (Z)-3-hexenal and its related compounds.
In the biochemical pathway for formation of (Z)-3-hexenal and its related compounds, lipoxygenase adds dioxygen at position 13 of linolenic acid to produce linolenic acid 13-hydroperoxide. The hydroperoxide is cleaved by hydroperoxide lyase at the C12–C13 bond to produce (Z)-3-hexenal, which can be reduced to form (Z)-3-hexenol. A portion of (Z)-3-hexenol is further converted to (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate. In some plants, (Z)-3-hexenal is converted to (E)-2-hexenal spontaneously or enzymatically. (Z)-3-Hexenal is spontaneously oxygenated to form 4-hydroperoxy-(E)-2-hexenal, 4-hydroxy-(E)-2-hexenal or 4-oxo-(E)-2-hexenal.