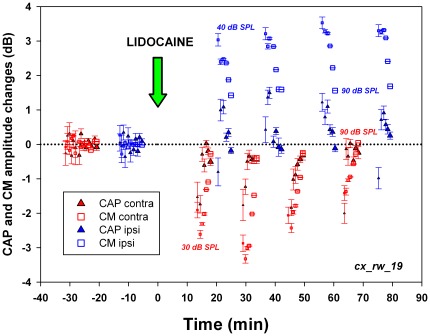
Figure 6. Temporal course and sound pressure dependence of bilateral cortico-olivocochlear effects after lidocaine cortical deactivation.
CM (squares) and CAP (triangles) amplitude changes are depicted in dB. Contralateral (right) and ipsilateral (left) cochlear potentials are depicted in red and blue respectively. In this experiment, 2 kHz stimuli were presented at different sound pressure levels, represented by symbol sizes increasing in 10 dB steps from 30–40 to 90 dB SPL. Significant contralateral reductions in CAP and CM (t = 4.20, p<0.01 and t = 6.47, p<0.01 respectively) and significant ipsilateral increases in CAP and CM (t = −2.21, p<0.05 and t = −12.64, p<0.001 respectively) were obtained. The largest effects on CM and CAP were found with low intensity sounds. Note that the sound pressure dependence of amplitude changes in CM and CAP for ipsi and contralateral cochlear electrical responses were in opposite directions (Exp_ID: cx_rw_19).