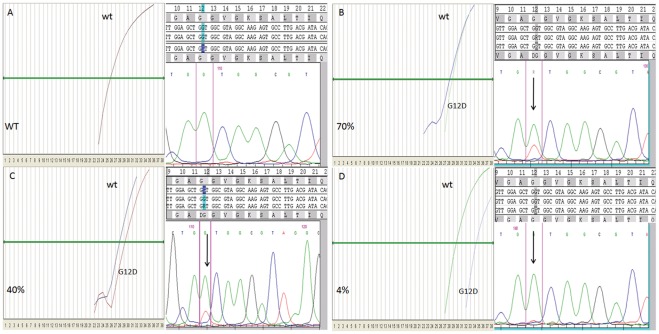
Figure 4. ASLNAqPCR and corresponding Sanger sequencing of four representative tumor samples analyzed for KRAS mutations.
Sample A is wild type, samples B, C and D are KRAS G12D mutated with varying amounts of tumor vs. non neoplastic cells; assuming that KRAS G12D is heterozygous, quantitation of mutated DNA by ASLNAqPCR (ΔCT method) is consistent with 70% of mutated cells in sample B, 40% of mutated cells in sample C, 4% of mutated cells in sample D; in sample D the KRAS G12D mutation is detected only by the ASLNAQPCR due to its high analytical sensitivity.