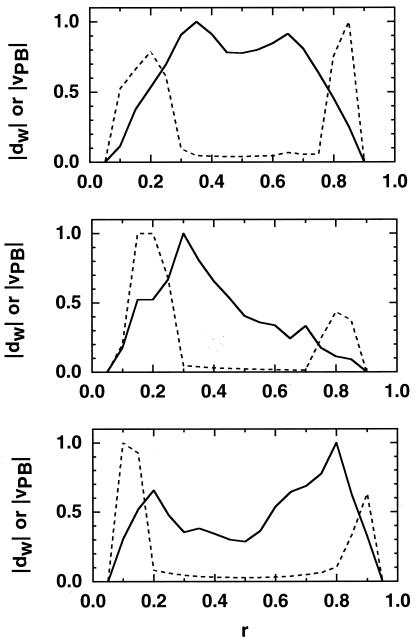
Figure 5.
Norm of time-averaged site-dipole, dw (w = 1 ns), and Poisson–Boltzmann's electrostatic field, vPB, along the line between two side-chain tips. The line was drawn from the side-chain tip of Asp (average position of OD1 and OD2) to that of Arg (that of NH1 and NH2). (A) System A, (B) system B, and (C) system C. Solid lines are the norm of dw and broken lines that of vPB. The x axis (r) is normalized by the distance between the side-chain tips (8 Å for system A and B, and 14 Å for system C) and the y axis is normalized by the largest norm along the line. The Poisson–Boltzmann equation was solved under the following condition: first, the two amino acids were put in a box (50 × 50 × 50 Å3) so that the water sphere (diameter = 50 Å) was included in the box. Next, the box was divided into the 1 Å cubes in the same manner as the evaluation of the site-dipoles. Lastly, vPB was calculated at each center of cubes. The dielectric constant was assumed to be 2.0 for cubes inside the amino acids, and 78.5 for those in the solvent region, where the Debye screening parameter was 0.0. The boundary of the box was calibrated by the self-consistent boundary method, by Green's function theorem (15), so that the electrostatic potential equals zero at infinity.