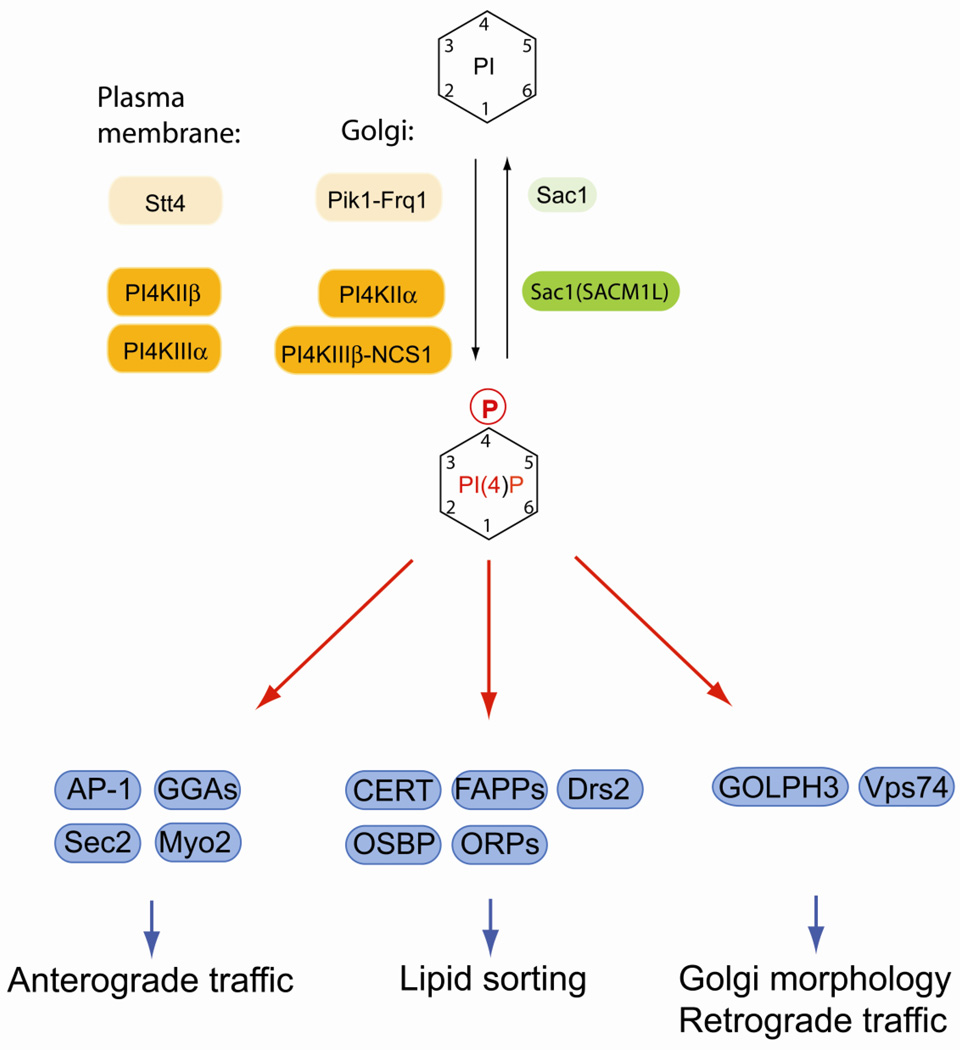
Fig. 3.
Regulation of PI(4)P and its essential function at the Golgi. In yeast, PI(4)P is synthesized by two essential PI 4-kinases, the Golgi-localized Pik1-Frq1 complex and plasma membrane Stt4. In mammalian cells, PI4KIIα and PI4KIIIβ generate Golgi PI(4)P, whereas PI4KIIβ and PI4KIIIα are involved in plasma membrane PI(4)P synthesis. Turnover and spatial control of PI(4)P is achieved by the evolutionary conserved lipid phosphatase Sac1 that also responds to nutrients and growth signals. Many effectors at the Golgi bind PI(4)P and regulate anterograde trafficking from the Golgi, resident enzyme recycling, lipid dynamics and sphingolipid biosynthesis. Mammalian lipid kinases or kinase complexes are marked by orange boxes, lipid phosphatases are in green boxes. Alternative names for certain enzymes are in parentheses. Yeast homologs are indicated by lighter shades of the same colors. Effector proteins are in blue boxes.