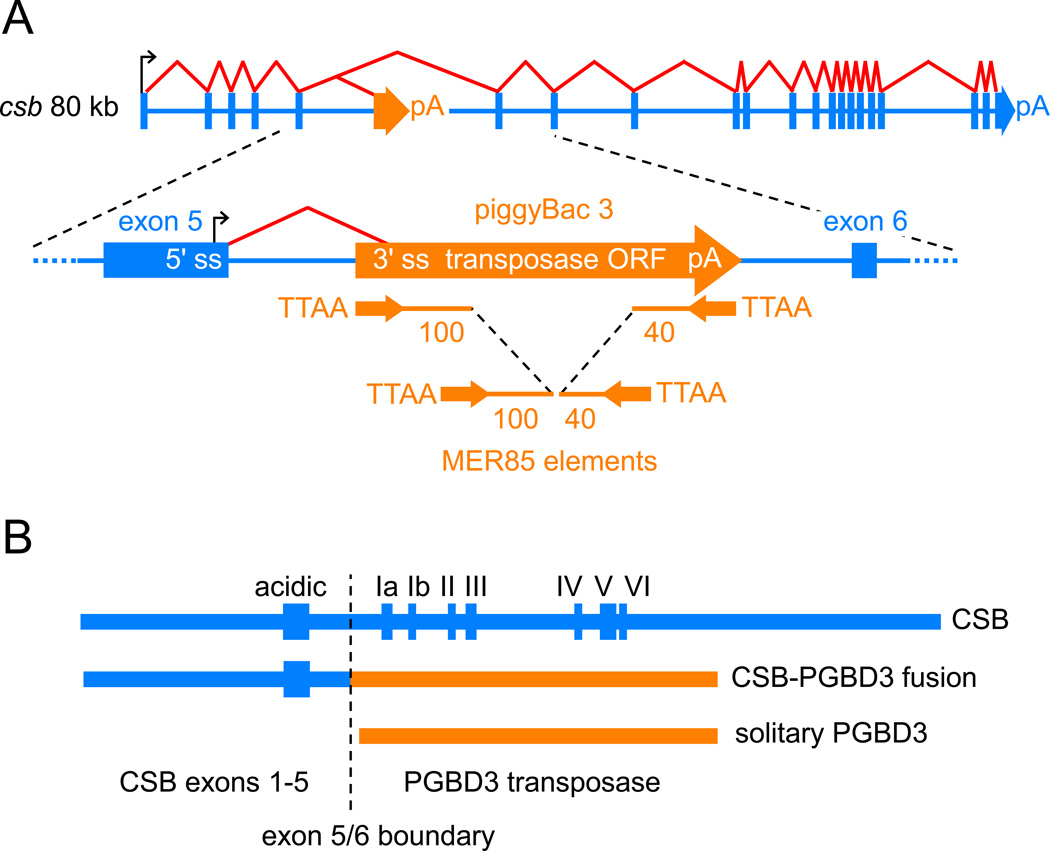
Fig. 1.
piggyBacs are mobile DNA elements that survive as alternative 3' exons. (A) PGBD3 inserted into intron 5 of the primate CSB gene at least 43 Mya in the common ancestor of simian primates, with the result that the CSB gene now generates three proteins as shown in (B): full length CSB by default splicing of all 22 CSB exons, CSB-PGBD3 fusion protein by alternative splicing between CSB exon 5 and the PGBD3 alternative 3' terminal exon, and solitary PGBD3 driven by a cryptic promoter in CSB exon 5 [18]. The PGBD3 insertion generated a TTAA target site duplication. Immediately inside the subterminal inverted repeats of the mobile element, the transposase open reading frame (ORF) is flanked upstream by a 3' splice site (3' ss) and downstream by a polyadenylation site (pA). MER85 elements are nonautonomous internally-deleted PGBD3-derived elements that were last mobilized by a PGBD3-like transposase about 35 Mya [19]. CSB and PGBD3 sequences are indicated in blue and orange, respectively. The schematic not drawn to scale; the CSB gene spans 80 kb, the PGBD3 element 2.5 kb, and intact MER85s only 140 bp. (B) A comparison of the three proteins encoded by the CSB locus. The fusion protein joins the acidic 465 N-terminal residues of CSB exons 1–5, but none of the ATPase motifs (Roman numerals), to the 595 residue PGBD3 transposase.