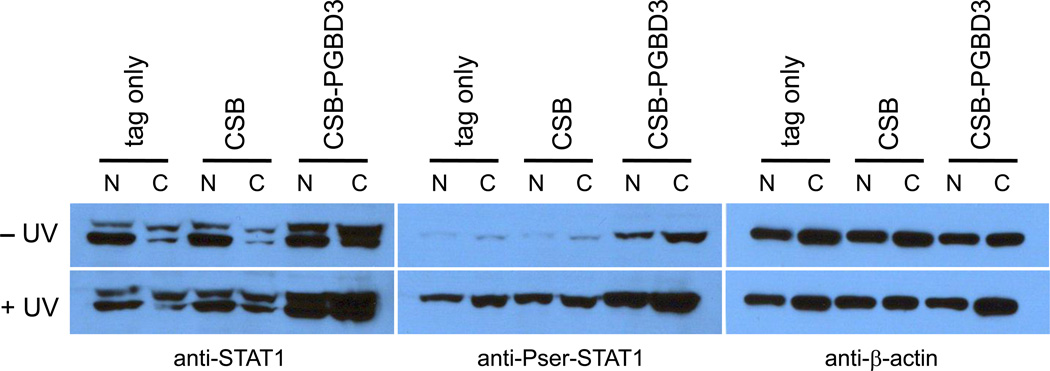
Fig. 3.
Expression of the CSB-PGBD3 fusion protein in CSB-null UVSS1KO cells induces U-STAT1, which can be phosphorylated on serine 727 and further induced by UV irradiation. Using CSB-null UVSS1KO cells stably transfected with CSB, CSB-PGBD3 fusion protein, or tags alone (Table 1), nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE, blotted, and probed with anti-STAT1 (left panel), anti-Pser-STAT1 (middle panel), and anti-β-actin antibodies as a loading control (right panel). The STAT1 locus generates two proteins (left panel): full length STAT1α (upper band) and C-terminally deleted STAT1β (lower band) lacking the Ser727 phosphorylation site. STAT1β has been referred to as a splice variant or proteolysis product [37]; however, mRNAs annotated on the UCSC Genome Browser (build hg18) indicate that STAT1β reflects alternative polyadenylation within intron 23. This results in use of a TAA terminator immediately following exon 23, and a protein that retains Tyr701 but lacks the Ser727 phosphorylation site.