Fig. 6.
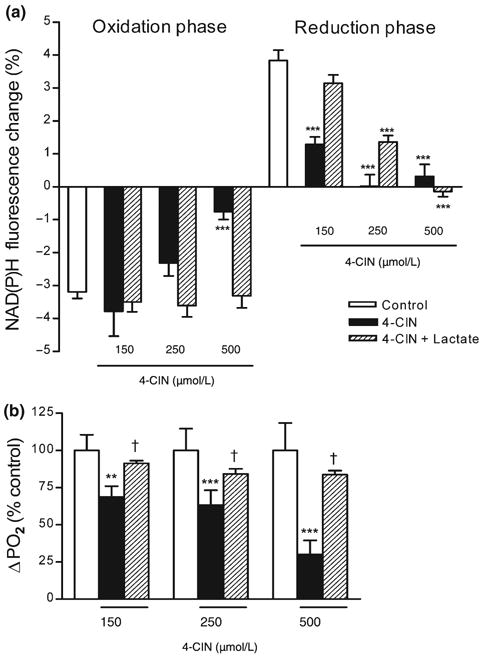
Effect of lactate supplementation on the NAD(P)H biphasic response and the tissue PO2 response in the presence of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamate (4-CIN). After synaptic stimulation hippocampal slices were supplemented with lactate (20 mmol/L) 10 min before the stimulus train in the presence of monocarboxylate transporter inhibitor 4-CIN. (a) Lactate restored the reduction phase of the NAD(P)H response in the presence of 4-CIN at lower concentrations. The early NAD(P)H oxidation phase was decreased only in the presence of 500 μmol/L 4-CIN and was restored to control levels by lactate supplementation. Data are the mean ± SEM of 5-35 slices. ***p < 0.001 versus control, †p < 0.05 versus 4-CIN (anova and Tukey's multicomparison test). (b) Lactate supplementation restored tissue PO2 response to control levels at all 4-CIN concentrations. Data are the mean ± SEM of 4-13 slices. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus control, †p < 0.05 versus 4-CIN (anova and Tukey's multicomparison test).
