Figure 5.
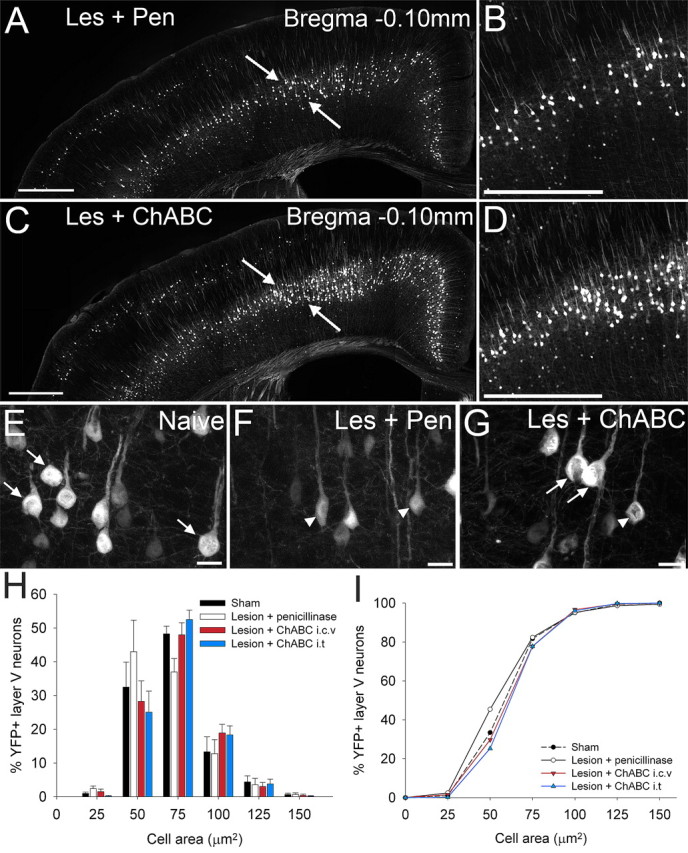
ChABC treatment, via two distinct methods of delivery, promotes neuroprotection of corticospinal projection neurons after spinal cord injury in the YFP-H mouse. In coronal sections through the YFP-H sensorimotor cortex at bregma −0.10 mm (A–I), representative low (A, C)- and high (B, D)-power images show many more large healthy YFP-labeled somata in the sensorimotor cortex after ChABC treatment (C, D) compared with penicillinase-treated animals (A, B). Higher-magnification images highlight the shift in cell size from large healthy cell somata in naive (uninjured) animals (E, arrows) to severely atrophied cells in injured animals treated with penicillinase (F, arrowheads). After injury and ChABC treatment (G), atrophy is apparent in only a small number of neurons (arrowheads), with the majority retaining normal cell sizes (arrows). Histogram (H) and cumulative frequency (I) plots confirm YFP-labeled CSNs in penicillinase-treated animals are significantly reduced in area compared with sham-operated animals (p < 0.05, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). ChABC treatment results in complete rescue of CSNs from injury induced atrophy at bregma −0.10, with the cell size distribution not significantly different from sham (p > 0.05, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). Cell size frequency distribution histograms display mean frequency ± SEM, n = 4 per treatment group. Scale bars: 500 μm (A, C), 250 μm (B, D), 20 μm (E, F, G).
