Figure 6.
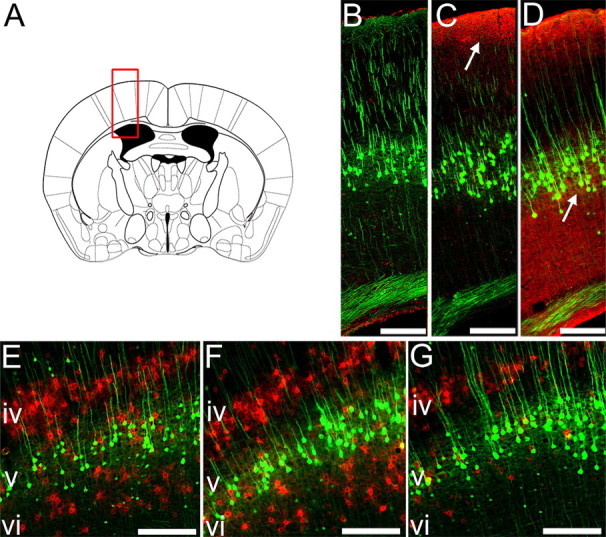
ICV but not IT delivery of ChABC degrades CSPGs close to layer V CSNs. Degradation of CSPGs in the sensorimotor cortex was evaluated at bregma −0.46 mm (A). Immunoreactivity for chondroitin-4-sulfate (C-4-S) epitopes (red) reveals degradation of matrix CSPGs after cleavage of sugar side chains by ChABC (B–D). Representative photomicrographs show no C-4-S immunoreactivity in the sensorimotor cortex of penicillinase-treated animals (B). After IT delivery of ChABC to the spinal injury site, CSPG digestion is only observed close to the pial surface (C, arrow). ICV delivery of ChABC (D, arrow) results in more extensive CSPG digestion in the cortex, including the area containing layer V YFP-labeled pyramidal neurons (green). Wisteria floribunda agglutinin histochemistry (E–G) reveals CSPGs within perineuronal nets in the sensorimotor cortex (red). Prominent labeling is observed in cortical layers IV and VI in penicillinase-treated animals (E). Labeling of PNNs is unchanged after IT delivery of ChABC (F), but ICV ChABC delivery results in a marked reduction in PNNs in cortical layer VI, close to the cell bodies of YFP-labeled layer V CSNs (G). Scale bars, 200 μm.
