Abstract
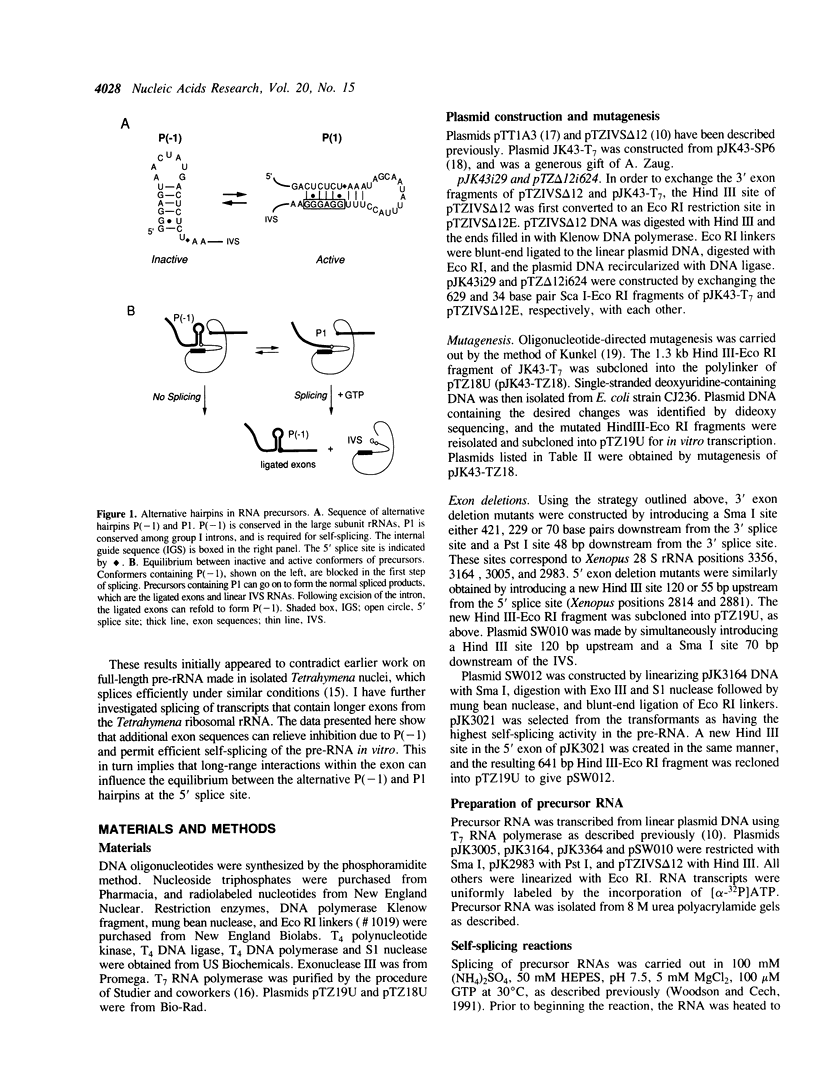
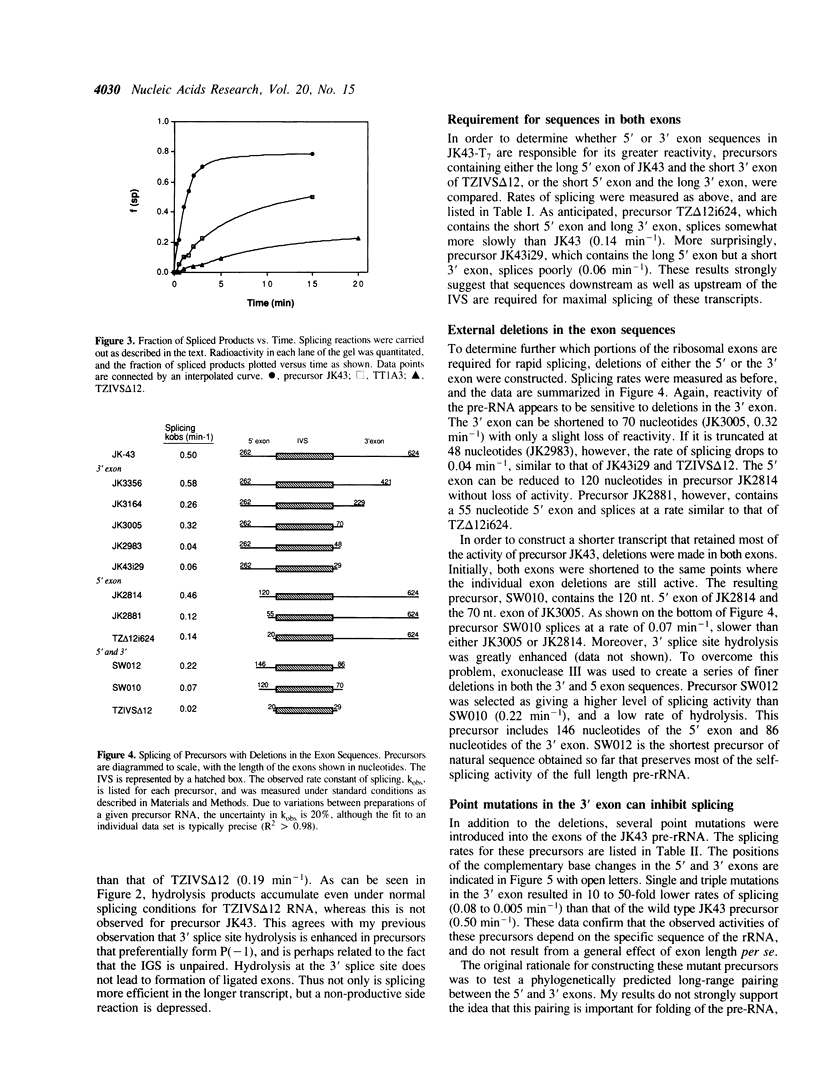
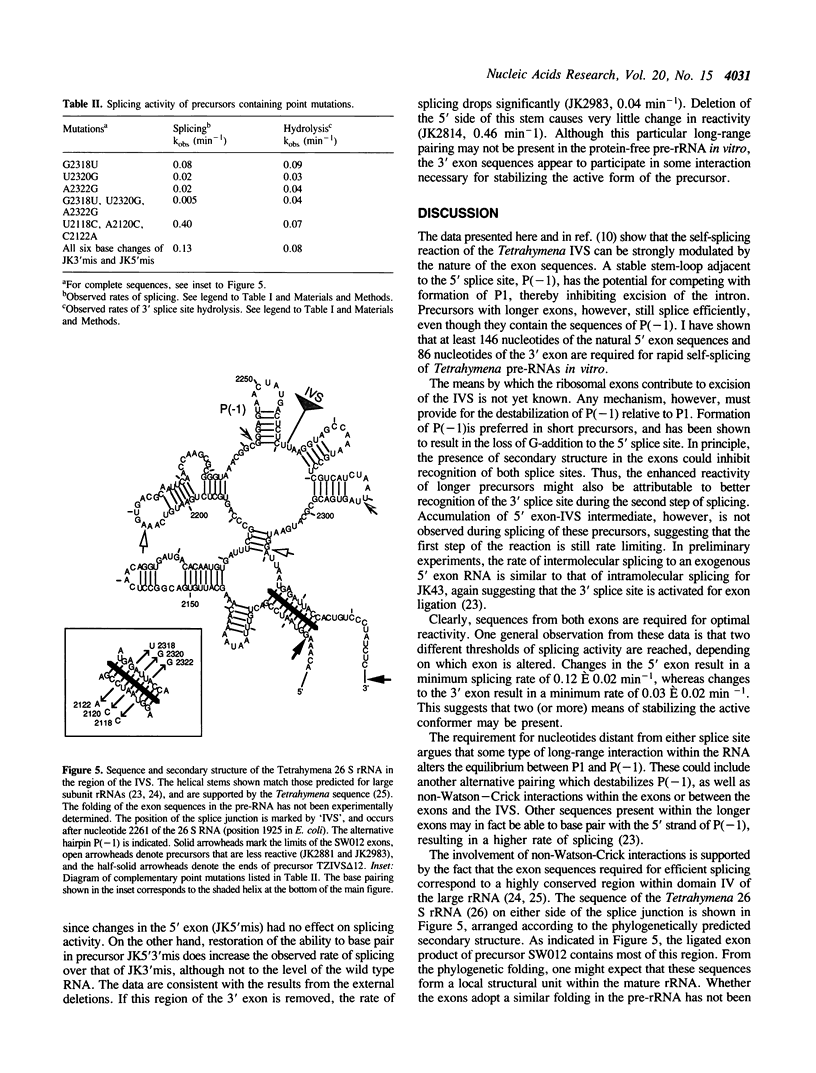
The presence of a natural rRNA secondary structure element immediately preceding the 5' splice site of the Tetrahymena IVS can inhibit self-splicing by competing with base pairing between the 5' exon and the guide sequence of the IVS (P1). Formation of this alternative hairpin is preferred in short precursor RNAs, and results in loss of G-addition to the 5' splice site. Pre-rRNAs which contain longer exons of ribosomal sequence, however, splice rapidly. As many as 146 nucleotides of the 5' exon and 86 nucleotides of the 3' exon are required for efficient self-splicing of Tetrahymena precursors. The presence of nucleotides distant from the 5' splice site apparently alters the equilibrium between the alternative hairpins, and promotes formation of active precursors. This effect is dependent on the specific sequences of the ribosomal pre-RNA, since point mutations within this region reduce the rate of splicing as much as 50-fold. This system provides an opportunity to study the way in which long-range interactions can influence splice site selection in a highly structured RNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Tague B. W., Ware V. C., Gerbi S. A. Xenopus laevis 28S ribosomal RNA: a secondary structure model and its evolutionary and functional implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6197–6220. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouet d'Orval B., d'Aubenton Carafa Y., Sirand-Pugnet P., Gallego M., Brody E., Marie J. RNA secondary structure repression of a muscle-specific exon in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1823–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.2063195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Nielsen H. Complete sequence of the extrachromosomal rDNA molecule from the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila strain B1868VII. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6915–6919. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. New reactions of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena and the mechanism of self-splicing. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Piseri A., Fiszman M. Y. Tissue-specific splicing in vivo of the beta-tropomyosin gene: dependence on an RNA secondary structure. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1842–1845. doi: 10.1126/science.2063196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. V., Kieft G. L., Kent J. R., Sievers E. L., Cech T. R. Sequence requirements for self-splicing of the Tetrahymena thermophila pre-ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1871–1889. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar M. B., Mertz J. E. Exon mutations that affect the choice of splice sites used in processing the SV40 late transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5591–5609. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodson S. A., Cech T. R. Alternative secondary structures in the 5' exon affect both forward and reverse self-splicing of the Tetrahymena intervening sequence RNA. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2042–2050. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. A labile phosphodiester bond at the ligation junction in a circular intervening sequence RNA. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):574–578. doi: 10.1126/science.6200938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]