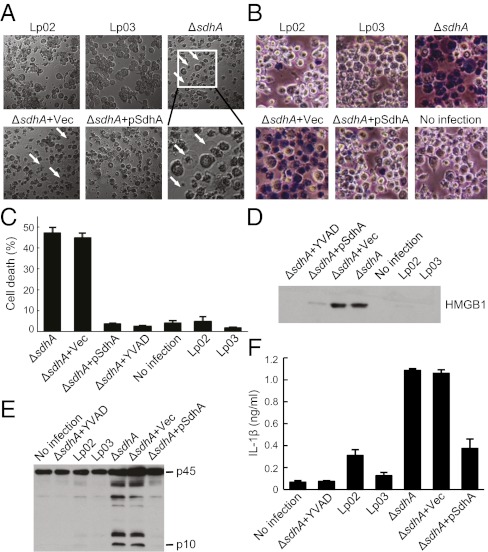
Fig. 1.
Deletion of sdhA triggers pyroptosis and caspase-1 activation in U937 cells. (A and B) Morphological examination of effects of sdhA deletion during L. pneumophila infection of PMA-differentiated U937 cells (MOI = 10). Lp02 is used as the wild-type strain; Lp03 is a dotA mutant. pSdhA is a complementation plasmid expressing SdhA. Differential interference contrast images (5 h after infection) are shown with cells stained with Trypan blue in B. Arrows indicate pyroptotic cells in A. (C and D) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (C) and HMGB1 (D) release assays of effects of sdhA deletion. Shown in C are percentages of cell death as mean values ± SD (error bars) from four independent experiments. Anti-HMGB1 immunoblot of culture media is shown in D. YVAD, a caspase-1 inhibitor. (E and F) Caspase-1 activation and IL-1β release assays of sdhA deletion. Shown in E is anti–caspase-1 immunoblot of culture supernatants. p45, procaspase-1; p10, the processed mature form of caspase-1. IL-1β ELISA data shown in F are as mean values ± SD (error bars) from three independent experiments.