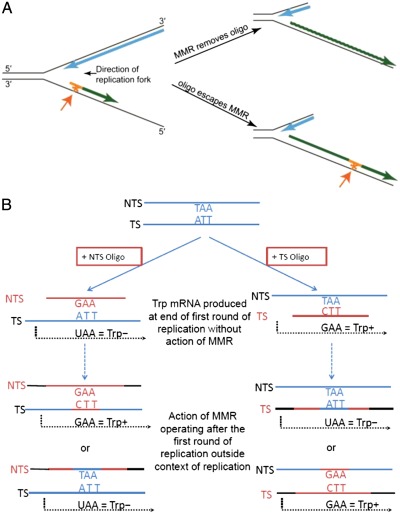
Fig. 1.
Model for transformation of trp5 G148T strains with TS or NTS oligos. (A) An oligo (orange) anneals at the replication fork, creating a mismatch (asterisk and orange arrow), and is extended to form an Okazaki fragment. MMR will remove the oligo, but if the oligo escapes MMR it will be incorporated into the genome. (B) An oligo (orange) is introduced into a cell and anneals with chromosomal DNA (blue). TAA is the NTS sequence of the mutant glutamic acid codon that must be mutated to GAA to give Trp+ revertants in the trp5 G148T strains. At the end of the first round of replication, Trp+ mRNA can be transcribed from the TS oligo, but RNA produced from transformation with a NTS oligo will still be Trp−. MMR correction operating outside the context of the replication fork after the first round of replication could result in two alternatives for each oligo, including Trp+ mRNA from an NTS oligo and Trp− mRNA from a TS oligo.