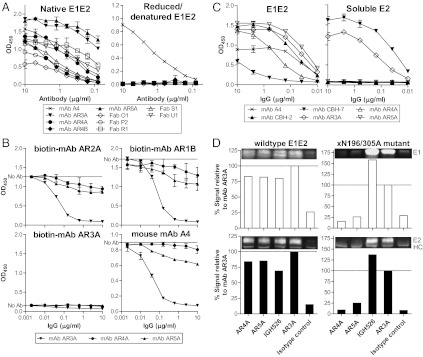
Fig. 1.
(A) The AR4- and AR5-specific antibodies recognize discontinuous epitopes on E1E2. E1E2 antigens (isolate H77) were denatured and reduced with SDS and DTT at 100 °C for 5 min. Native or reduced/denatured E1E2 was probed with the antibodies at the specified concentrations in ELISA. The murine mAb A4 (47), specific for E1 residues 197–207, was a positive control for reduced/denatured E1. (B) AR4 and AR5 do not overlap with CD81bs on E1E2. The effect of mAbs AR4A and AR5A on the binding of E1E2 to the large extracellular loop of CD81 (CD81-LEL) was studied by ELISA. E1E2 antigens (isolate H77) were preincubated with serially diluted mAbs AR3A, AR4A, or AR5A before being added to ELISA wells coated with CD81-LEL (fused to maltose-binding protein). Bound E1E2 was detected with biotinylated mAbs AR1B, AR2A, AR3A, or murine mAb A4. Note that the epitope recognized by mAb AR3A, but not the other three mAbs, overlaps with E1E2 CD81bs. Therefore, only mAb AR3A significantly inhibited the interaction between E1E2 and CD81-LEL. (C) Binding of mAbs AR3A, AR4A, and AR5A to lectin-captured full-length E1E2 (Left) and E2 with the transmembrane domain truncated (soluble E2; Right). The control antibodies are murine mAb A4, mAbs CBH-7 (19), and AR3A (11), recognizing discontinuous epitopes on E2, and mAb CBH-2, recognizing an epitope on the E1E2 heterodimer (35). (D) Immunoprecipitation of E1E2 complex by mAbs AR4A and AR5A. The wild-type and xN196/305A mutant E1E2 were pulled down by using mAbs AR4A and AR5A, the anti-E1 mAb IGH526 (14), the anti-E2 mAb AR3A, the isotype control anti-HIV mAb b6 (11), and protein A-conjugated agarose. The immunoprecipitants were analyzed by reducing SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting using mAb A4 for E1 (47) and mAb HCV1 for E2 (8). The amounts of E1 and E2 pulled down by the antibodies were compared with that of mAb AR3A. HC, antibody heavy chain.