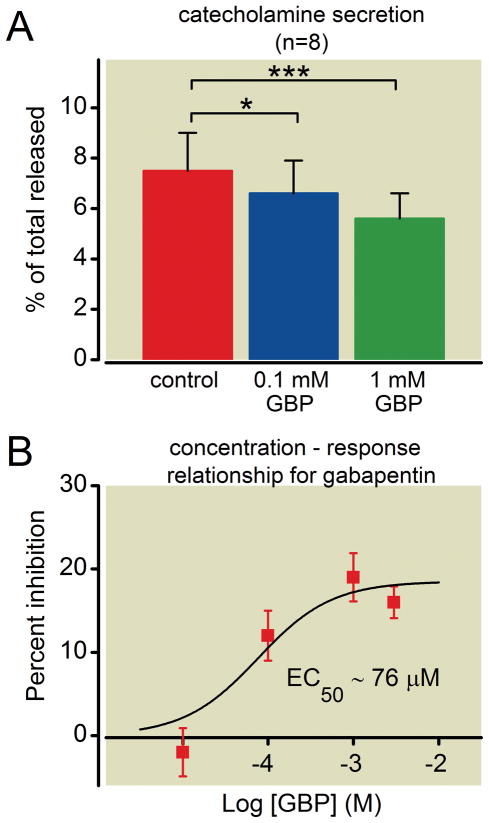
Figure 3. The inhibition of catecholamine secretion by gabapentin is concentration-dependent.
(A) Chromaffin cells were seeded on 24-well plates and treated with vehicle (control) or gabapentin (0.1mM GBP or 1mM GBP) for 18–24 h. Evoked catecholamine secretion was determined using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and expressed as a percentage of total cellular content (mean ± SEM). Both concentrations of gabapentin significantly reduced secretion compared to controls (n = 8; * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001). (B) Data from all HPLC experiments were pooled and percent inhibition of evoked catecholamine secretion (mean ± SEM) plotted against Log 10 of gabapentin concentration (10 μM, n = 4; 100 μM, n = 8; 1mM, n = 20; 3 mM, n = 4). A concentration response curve was generated by fitting the data to a Boltzmann function with a Hill slope = 1, and yielded an estimated EC50 of 76 μM.