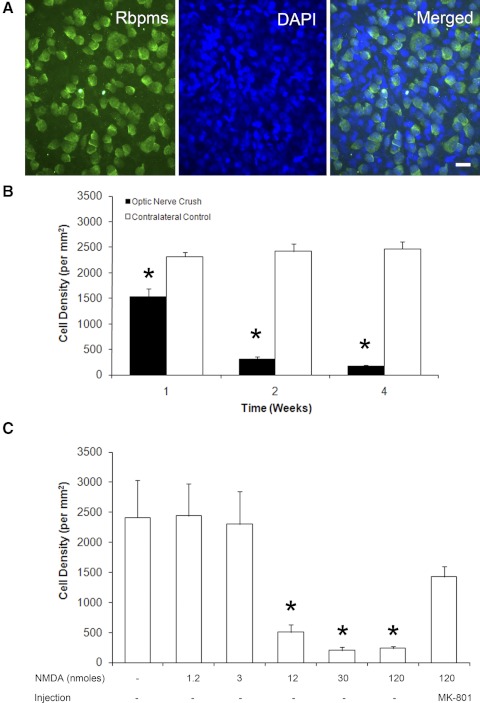
Figure 2.
Temporal- and dose-dependent loss of Rbpms-positive cells after optic nerve crush and excitotoxicity, respectively. (A) Wholemount retinas were immunostained with Rbpms antibodies and counterstained with DAPI to visualize cell nuclei. Rbpms-positive cells make up only a portion of all cells in the retinal ganglion cell layer (RGCL), since rodent RGCL contains both RGCs and displaced amacrine cells in an approximately equal ratio. (B) The density of Rbpms-positive cells after optic nerve crush compared with contralateral control. Progressive loss of RGCs 1 week (37%), 2 weeks (87%), and 4 weeks (93%) after optic nerve injury were observed. (C) Significant decreases of Rbpms-positive cell density were noted 1 week after intravitreal injection of 12, 30, and 120 nmol NMDA. Injection of MK-801 reduced the excitotoxic effect of NMDA (120 nmol) RGCs.